-
Latest Version
-
Operating System
Windows Vista64 / Windows 7 64 / Windows 8 64 / Windows 10 64 / Windows 11
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
python-3.13.1.amd64.exe
Sometimes latest versions of the software can cause issues when installed on older devices or devices running an older version of the operating system.
Software makers usually fix these issues but it can take them some time. What you can do in the meantime is to download and install an older version of Python 3.13.1 (64-bit).
For those interested in downloading the most recent release of Python (64-bit) or reading our review, simply click here.
All old versions distributed on our website are completely virus-free and available for download at no cost.
We would love to hear from you
If you have any questions or ideas that you want to share with us - head over to our Contact page and let us know. We value your feedback!
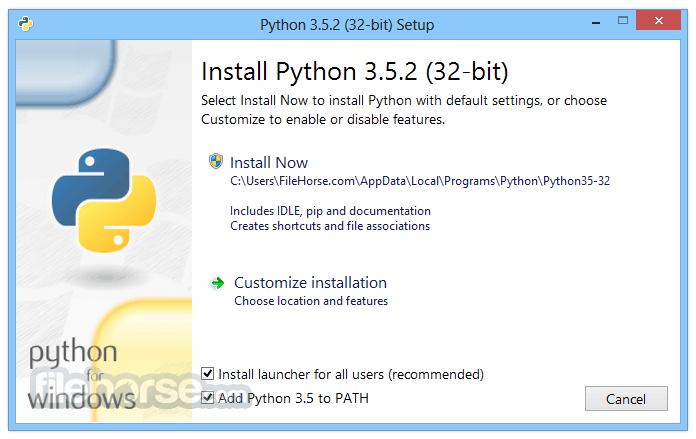
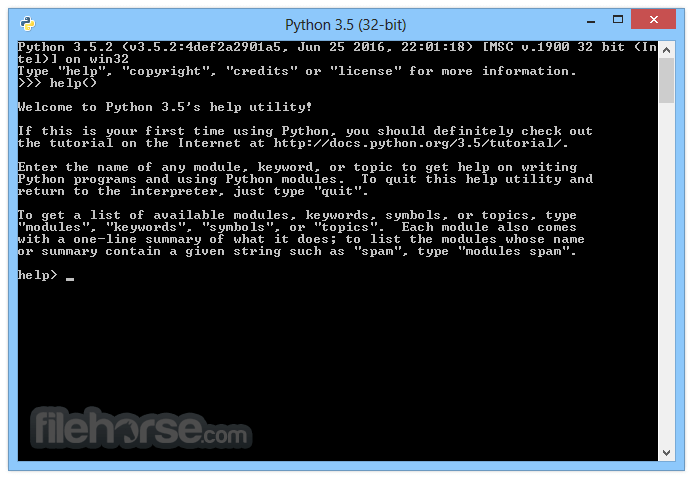
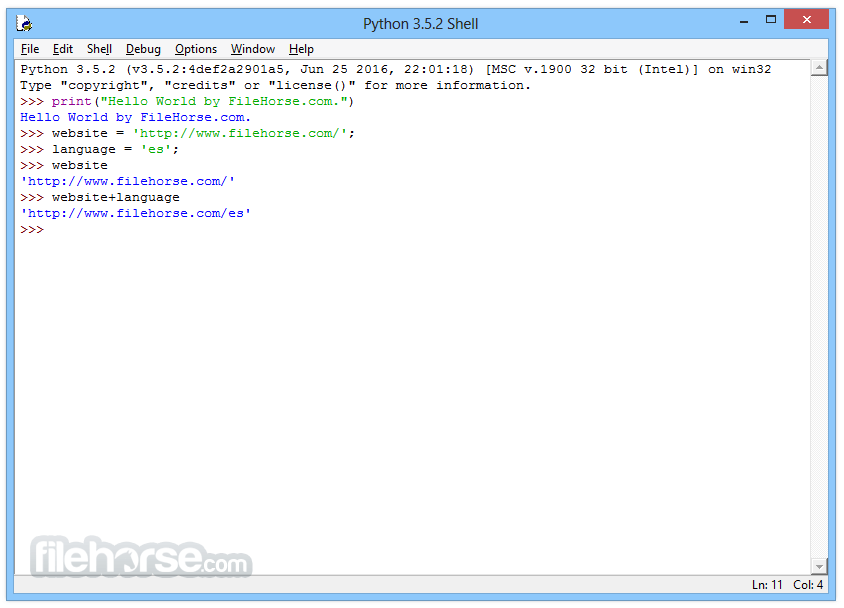
What's new in this version:
- Update credits command output.
- Ensures the experimental free-threaded install includes the _tkinter module. The optional Tcl/Tk component must also be installed in order for the module to work.
- Fixes venv failure due to missing redirector executables in experimental free-threaded installs.
- Removed unnecessary DLLs from Windows embeddable package
- Avoid crashing in platform due to slow WMI calls on some Windows machines.
- Fix venvwlauncher to launch pythonw instead of python so no extra console window is created.
- Fix a SystemError when sys.exit() is called with 0xffffffff on Windows.
- Enable the Python Launcher for Windows to detect Python 3.14 installs from the Windows Store.
- Updated bundled Tcl/Tk to 8.6.15.
Tools/Demos:
- Fix extraction warnings in pygettext.py caused by mistaking function definitions for function calls.
- The iOS testbed was modified so that it can be used by third-party projects for testing purposes.
Tests:
- Fix test_os extended attribute tests to work on filesystems with 1 KiB xattr size limit.
- Re-enable skipped tests for zlib on the s390x architecture: only skip checks of the compressed bytes, which can be different between zlib’s software implementation and the hardware-accelerated implementation.
- Add translation tests to the argparse module.
Security:
- Upgrade libexpat to 2.6.4
- Remove the current directory from sys.path when using PyREPL.
- Changed IPv4-mapped ipaddress.IPv6Address to consistently use the mapped IPv4 address value for deciding properties. Properties which have their behavior fixed are is_multicast, is_reserved, is_link_local, is_global, and is_unspecified.
Library:
- pdb.set_trace() will not stop at an opcode that does not have an associated line number anymore.
- Publicly expose EXACT_TOKEN_TYPES in token.__all__.
- Fix faulthandler for trampoline frames. If the top-most frame is a trampoline frame, skip it. Patch by Victor Stinner.
- Fix io.StringIO.__setstate__() crash, when None was passed as the first value.
- Fix urllib.request.pathname2url() for paths starting with multiple slashes on Posix.
- Fix shutil.which on Windows. Now it looks at direct match if and only if the command ends with a PATHEXT extension or X_OK is not in mode. Support extensionless files if “.” is in PATHEXT. Support PATHEXT extensions that end with a dot.
- Support PyREPL history on Windows. Patch by devdanzin and Victor Stinner.
- Fix issue where urllib.request.url2pathname() failed to discard an extra slash before a UNC drive in the URL path on Windows.
- Fix issue where urllib.request.url2pathname() failed to discard any ‘localhost’ authority present in the URL.
- Fix crash when calling a operator.methodcaller() instance from multiple threads in the free threading build.
- Fix support of STRING and GLOBAL opcodes with non-ASCII arguments in pickletools. pickletools.dis() now outputs non-ASCII bytes in STRING, BINSTRING and SHORT_BINSTRING arguments as escaped (\xXX).
- grp: Make grp.getgrall() thread-safe by adding a mutex. Patch by Victor Stinner.
- Fix the representation of itertools.count objects when the count value is sys.maxsize.
-Fix issue where urllib.request.url2pathname() and pathname2url() always used UTF-8 when quoting and unquoting file URIs. They now use the filesystem encoding and error handler.
-Fix memory leaks when regular expression matching terminates abruptly, either because of a signal or because memory allocation fails.
- Fixed the values of sysconfig.get_config_vars(), sysconfig.get_paths(), and their siblings when the site initialization happens after sysconfig has built a cache for sysconfig.get_config_vars().
- Update bundled pip to 24.3.1
- Fix os.path.normpath() for drive-relative paths on Windows.
- Fix issue where urllib.request.url2pathname() failed to discard two leading slashes introducing an empty authority section.
- locale.nl_langinfo(locale.ERA) now returns multiple era description segments separated by semicolons. Previously it only returned the first segment on platforms with Glibc.
- Allow collections.abc.AsyncIterator to be a base for Protocols.
- Fix crash when non-dict was passed to several functions in _interpreters module.
- Limit starting a patcher (from unittest.mock.patch() or unittest.mock.patch.object()) more than once without stopping it
- Fix a crash when instantiating itertools.count with an initial count of sys.maxsize on debug builds. Patch by Bénédikt Tran.
- Fix issue where urllib.request.pathname2url() mishandled Windows paths with embedded forward slashes.
- Improve performances of zipfile.Path.open() for non-reading modes.
- Fix bugs in compiling case-insensitive regular expressions with character classes containing non-BMP characters: upper-case non-BMP character did was ignored and the ASCII flag was ignored when matching a character range whose upper bound is beyond the BMP region.
- Fixed the multiprocessing "forkserver" start method forkserver process to correctly inherit the parent’s sys.path during the importing of multiprocessing.set_forkserver_preload() modules in the same manner as sys.path is configured in workers before executing work items.
- This bug caused some forkserver module preloading to silently fail to preload. This manifested as a performance degration in child processes when the sys.path was required due to additional repeated work in every worker.
- It could also have a side effect of "" remaining in sys.path during forkserver preload imports instead of the absolute path from os.getcwd() at multiprocessing import time used in the worker sys.path.
- The sys.path differences between phases in the child process could potentially have caused preload to import incorrect things from the wrong location. We are unaware of that actually having happened in practice.
- The multiprocessing.Lock and multiprocessing.RLock repr values no longer say “unknown” on macOS.
- Raise calendar.IllegalMonthError (now a subclass of IndexError) for calendar.month() when the input month is not correct.
- The Python implementation of pickle no longer calls pickle.Pickler.persistent_id() for the result of persistent_id().
- Fix an issue in curses.napms() when curses.initscr() has not yet been called. Patch by Bénédikt Tran.
- Fix pickling and copying of os.sched_param objects.
- Fix a use-after-free crash on asyncio.Task objects whose underlying coroutine yields an object that implements an evil __getattribute__(). Patch by Nico Posada.
- Fix crash in cProfile.Profile and _lsprof.Profiler when their callbacks were directly called with 0 arguments.
- Fix issue where urllib.request.pathname2url() and url2pathname() removed slashes from Windows DOS drive paths and URLs.
- Raise a UnicodeEncodeError instead of a SystemError upon calling _interpreters.create() with an invalid Unicode character.
- Fix issue where urllib.request.pathname2url() generated URLs beginning with four slashes (rather than two) when given a Windows UNC path.
- Fix a crash in ast when the ast.AST._fields attribute is deleted.
- Fixes a possible NULL pointer dereference in ssl.
- Fix a use-after-free crash on asyncio.Task objects for which the underlying event loop implements an evil __getattribute__(). Reported by Nico-Posada. Patch by Bénédikt Tran.
- Fixed a reference leak in asyncio.Task objects when reinitializing the same object with a non-None context. Patch by Nico Posada.
- Fix use-after-free crashes on asyncio.Future objects for which the underlying event loop implements an evil __getattribute__(). Reported by Nico-Posada. Patch by Bénédikt Tran.
- Fix an out-of-bounds crash when an evil asyncio.loop.call_soon() mutates the length of the internal callbacks list. Patch by Bénédikt Tran.
- Fix a use-after-free crash in asyncio.Future.remove_done_callback(). Patch by Bénédikt Tran.
- Fix possible crash when mutating list of callbacks returned by asyncio.Future._callbacks. It now always returns a new copy in C implementation _asyncio. Patch by Kumar Aditya.
- Fix an issue in email.policy.EmailPolicy.header_source_parse() and email.policy.Compat32.header_source_parse() that introduced spurious leading whitespaces into header values when the header includes a newline character after the header name delimiter (:) and before the value.
- Fixed the bug for pdb where it can’t set breakpoints on functions with certain annotations.
- Fix several bugs in argparse.ArgumentParser.parse_intermixed_args().
- The parser no longer changes temporarily during parsing.
- Default values are not processed twice.
- Required mutually exclusive groups containing positional arguments are now supported.
- The missing arguments report now includes the names of all required optional and positional arguments.
- Unknown options can be intermixed with positional arguments in parse_known_intermixed_args().
- Avoid the exiting the interpreter if a null byte is given as input in the new REPL.
- [Enum] fix hashable<->nonhashable comparisons for member values
- Restore ability to set persistent_id and persistent_load attributes of instances of the Pickler and Unpickler classes in the pickle module.
- Fixed the bug in pdb where after a multi-line command, an empty line repeats the first line of the multi-line command, instead of the full command.
- Reject non-ASCII digits in the Python implementation of json.loads() conforming to the JSON specification.
- Reject invalid unicode escapes for Python implementation of json.loads().
- Fix the notes removal logic for errors thrown in enum initialization.
- Allow FrameLocalsProxy to delete and pop if the key is not a fast variable.
- Improve traceback if importlib.reload() is called with an object that is not a module. Patch by Alex Waygood.
- Fix deadlock when concurrent.futures.ProcessPoolExecutor shuts down concurrently with an error when feeding a job to a worker process.
- Fixed the bug where pdb and bdb can step into the bottom caller frame.
- Fixed the bug where pdb will be stuck in an infinite loop when debugging an empty file.
- Fixed a bug in pdb where arguments starting with - can’t be passed to the debugged script.
-Fix time.strptime() for %c, %x and %X formats in many locales that use non-ASCII digits, like Persian, Burmese, Odia and Shan.
- Fix the conversion of the VIRTUAL_ENV path in the activate script in venv when running in Git Bash for Windows.
- Fix using functools.partial() as enum.Enum member. A FutureWarning with suggestion to use enum.member() is now emitted when the partial instance is used as an enum member.
- Fix race condition when importing collections.abc, which could incorrectly return an empty module.
- Fix data race when creating zoneinfo.ZoneInfo objects in the free threading build.
- Fix a bug where ArgumentError includes the incorrect ambiguous option in argparse.
- Keep tkinter TCL paths in venv pointing to base installation on Windows.
-Fix inheritance of nested mutually exclusive groups from parent parser in argparse.ArgumentParser. Previously, all nested mutually exclusive groups lost their connection to the group containing them and were displayed as belonging directly to the parser.
-Fix encoding issues in time.strftime(), the strftime() method of the datetime classes datetime, date and time and formatting of these classes. Characters not encodable in the current locale are now acceptable in the format string. Surrogate pairs and sequence of surrogatescape-encoded bytes are no longer recombinated. Embedded null character no longer terminates the format string.
- Don’t copy arbitrary values to _Bool in the struct module.
- Fix an issue where providing a pathlib.PurePath object as an initializer argument to a second PurePath object with a different parser resulted in arguments to the former object’s initializer being joined by the latter object’s parser.
- If the PYTHON_BASIC_REPL environment variable is set, the site module no longer imports the _pyrepl module. Moreover, the site module now respects -E and -I command line options: ignore PYTHON_BASIC_REPL in this case. Patch by Victor Stinner.
- Fix locale.nl_langinfo(locale.ALT_DIGITS) on platforms with glibc. Now it returns a string consisting of up to 100 semicolon-separated symbols (an empty string in most locales) on all Posix platforms. Previously it only returned the first symbol or an empty string.
- Fix support for the barry_as_FLUFL future flag in the new REPL.
- Fixed thread safety in ssl in the free-threaded build. OpenSSL operations are now protected by a per-object lock.
- Fix refcycles in exceptions raised from asyncio.TaskGroup and the python implementation of asyncio.Future
-Fix time.strptime() for %c and %x formats in many locales: Arabic, Bislama, Breton, Bodo, Kashubian, Chuvash, Estonian, French, Irish, Ge’ez, Gurajati, Manx Gaelic, Hebrew, Hindi, Chhattisgarhi, Haitian Kreyol, Japanese, Kannada, Korean, Marathi, Malay, Norwegian, Nynorsk, Punjabi, Rajasthani, Tok Pisin, Yoruba, Yue Chinese, Yau/Nungon and Chinese.
- Allow calling os.path.exists() and os.path.lexists() with keyword arguments on Windows. Fixes a regression in 3.13.0.
- Fix detection of the minimal Queue API needed by the logging module. Patch by Bénédikt Tran.
- Fix reference cycles left in tracebacks in asyncio.open_connection() when used with happy_eyeballs_delay
- Fixed AssertionError when using asyncio.staggered.staggered_race() with asyncio.eager_task_factory.
- Properly quote template strings in venv activation scripts.
- Fix argparse for namespaces with not directly writable dict (e.g. classes).
-Fix conflicts between abbreviated long options in the parent parser and subparsers in argparse.
- All asyncio REPL prompts run in the same context. Contributed by Bartosz Sławecki.
-Fix support of choices with string value in argparse. Substrings of the specified string no longer considered valid values.
-Fix argparse support of positional arguments with nargs='?', default=argparse.SUPPRESS and specified type.
- Fix a crash related to an integer overflow in curses.resizeterm() and curses.resize_term().
- Fixed bug in itertools.tee() handling of other tee inputs (a tee in a tee). The output now has the promised n independent new iterators. Formerly, the first iterator was identical (not independent) to the input iterator. This would sometimes give surprising results.
-Fixed a bug in pdb where sometimes the breakpoint won’t trigger if it was set on a function which is already in the call stack.
- argparse vim supports abbreviated single-dash long options separated by = from its value.
- Fix disallowing abbreviation of single-dash long options in argparse with allow_abbrev=False.
-Fix parsing mutually exclusive arguments in argparse. Arguments with the value identical to the default value (e.g. booleans, small integers, empty or 1-character strings) are no longer considered “not present”.
-Positional arguments with nargs equal to '*' or argparse.REMAINDER are no longer required. This allows to use positional argument with nargs='*' and without default in mutually exclusive group and improves error message about required arguments.
-Fix parsing positional argument with nargs equal to '?' or '*' if it is preceded by an option and another positional argument.
-argparse now ignores the first "--" (double dash) between an option and command.
- Add RFC 9637 reserved IPv6 block 3fff::/20 in ipaddress module.
-Fix handling of multiple "--" (double dashes) in argparse. Only the first one has now been removed, all subsequent ones are now taken literally.
- Remove broken time.thread_time() and time.thread_time_ns() on NetBSD.
- Fix possible crash (in debug build), incorrect output or returning incorrect value from raw binary write() when writing to console on Windows.
- Fix parent slots detection for dataclasses that inherit from classes with __dictoffset__.
- Fix unbalanced quote errors occurring when activate.csh in venv was sourced with a custom prompt containing unpaired quotes or newlines.
- Fix the canvas not clearing after running turtledemo clock.
- Resolve a memory leak introduced in CPython 3.10’s ssl when the ssl.SSLSocket.session property was accessed. Speeds up read and write access to said property by no longer unnecessarily cloning session objects via serialization.
- Update unbounded read calls in zipfile to specify an explicit size putting a limit on how much data they may read. This also updates handling around ZIP max comment size to match the standard instead of reading comments that are one byte too long.
-Fixed an issue where inspect.getclosurevars() would incorrectly classify an attribute name as a global variable when the name exists both as an attribute name and a global variable.
- posixpath.realpath() now raises NotADirectoryError when strict mode is enabled and a non-directory path with a trailing slash is supplied.
- Always return an absolute path for os.path.abspath() on Windows.
- Always use str() to print choices in argparse.
- Fix SystemError when match regular expression pattern containing some combination of possessive quantifier, alternative and capture group.
-Fixed multiprocessing.Process reporting a .exitcode of 1 even on success when using the "fork" start method while using a concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor.
-Fix a race condition in multiprocessing.pool.Pool.
- bpo-46128: Strip unittest.IsolatedAsyncioTestCase stack frames from reported stacktraces.
- bpo-14074: Fix argparse metavar processing to allow positional arguments to have a tuple metavar.
IDLE:
- Increase currently inadequate vertical spacing for the IDLE browsers (path, module, and stack) on high-resolution monitors.
Documentation:
- Added stub pages for removed modules explaining their removal, where to find replacements, and linking to the last Python version that supported them. Contributed by Ned Batchelder.
- Require Sphinx 7.2.6 or later to build the Python documentation. Patch by Adam Turner.
- Added definitions for context, current context, and context management protocol, updated related definitions to be consistent, and expanded the documentation for contextvars.Context.
- The importlib.metadata documentation now includes semantic cross-reference targets for the significant documented APIs. This means intersphinx references like importlib.metadata.version() will now work as expected.
-Clarified the dual usage of the term “free variable” (both the formal meaning of any reference to names defined outside the local scope, and the narrower pragmatic meaning of nonlocal variables named in co_freevars).
- Writers of CPython’s documentation can now use next as the version for the versionchanged, versionadded, deprecated directives.
-Include the object type in the lists of documented types
- bpo-34008: The Py_Main() documentation moved from the “Very High Level API” section to the “Initialization and Finalization” section.
- Also make it explicit that we expect Py_Main to typically be called instead of Py_Initialize rather than after it (since Py_Main makes its own call to Py_Initialize). Document that calling both is supported but is version dependent on which settings will be applied correctly.
Core and Builtins:
- Fix possible undefined behavior division by zero in complex’s _Py_c_pow().
- Fix a crash in the free threading build when PyCode_GetCode(), PyCode_GetVarnames(), PyCode_GetCellvars(), or PyCode_GetFreevars() were called from multiple threads at the same time.
- Fix __buffer__() of bytearray crashing when READ or WRITE are passed as flags.
- Fix crash in finalization of dtoa state. Patch by Kumar Aditya.
- Now ValueError is raised instead of SystemError when trying to iterate over a released memoryview object.
- Fix a crash when calling os.fork() on some operating systems, including SerenityOS.
- Fix importlib to not write an incomplete .pyc files when a ulimit or some other operating system mechanism is preventing the write to go through fully.
- Fix crash during garbage collection on an object frozen by gc.freeze() on the free-threaded build.
- Provide better error location when attempting to use a future statement with an unknown future feature.
- Fix a crash in sys.audit() when passing a non-string as first argument and Python was compiled in debug mode.
- On Android, the errors setting of sys.stdout was changed from surrogateescape to backslashreplace.
- Fix a crash in the free threading build when gc.get_objects() or gc.get_referrers() is called during an in-progress garbage collection.
- Correctly honour tracemalloc hooks in specialized Py_DECREF paths. Patch by Pablo Galindo
- Use color to highlight error locations in traceback from exception group
- Fix illegal instruction for older Arm architectures. Patch by Diego Russo, testing by Ross Burton.
- Fix a crash in the free threading build when the GC runs concurrently with a new thread starting.
- Fix possible race condition when calling __reduce_ex__() for the first time in the free threading build.
- Fix crash when iterating over a generator expression after direct changes on gi_frame.f_locals. Patch by Mikhail Efimov.
- Fix a crash in the __str__() method of UnicodeError objects when the UnicodeError.start and UnicodeError.end values are invalid or out-of-range. Patch by Bénédikt Tran.
- Fix a crash caused by immortal interned strings being shared between sub-interpreters that use basic single-phase init. In that case, the string can be used by an interpreter that outlives the interpreter that created and interned it. For interpreters that share obmalloc state, also share the interned dict with the main interpreter.
- Use the pager binary, if available (e.g. on Debian and derivatives), to display REPL help().
- Fix reading and decoding a line from the source file witn non-UTF-8 encoding for syntax errors raised in the compiler.
- Improve the error message when a script shadowing a module from the standard library causes ImportError to be raised during a “from” import. Similarly, improve the error message when a script shadowing a third party module attempts to “from” import an attribute from that third party module while still initialising.
- Building with HAVE_DYNAMIC_LOADING now works as well as it did in 3.12. Existing deficiences will be addressed separately
- Fix bug where SSLProtocol.connection_lost wasn’t getting called when OSError was thrown on writing to socket.
- Fixed a bug in reprlib.repr where it incorrectly called the repr method on shadowed Python built-in types.
- If _thread.start_new_thread() fails to start a new thread, it deletes its state from interpreter and thus avoids its repeated cleanup on finalization.
C API:
- Fix error handling in ctypes.CDLL objects which could result in a crash in rare situations.
- Fix a bug where dictionary watchers (e.g., PyDict_Watch()) on an object’s attribute dictionary (__dict__) were not triggered when the object’s attributes were modified.
- bpo-34008: Added Py_IsInitialized to the list of APIs that are safe to call before the interpreter is initialized, and updated the embedding tests to cover it.
Build:
- Set wasm32-wasip1 as the WASI target. The old wasm32-wasi target is deprecated so it can be used for an eventual WASI 1.0.
-Hard-code float word ordering as little endian on WASM.
- The Android build now supports 16 KB page sizes.
-Improve detection of float word ordering on Linux when link-time optimizations are enabled.
- Fix detection of whether -latomic is needed when cross-compiling CPython using the configure script.
- Allow for specifying the target compile triple for WASI.
- Use WASI SDK 24 for testing.
- Fix cross compile failures when the host and target SOABIs match.
 OperaOpera 125.0 Build 5729.49 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 125.0 Build 5729.49 (64-bit) MalwarebytesMalwarebytes Premium 5.4.5
MalwarebytesMalwarebytes Premium 5.4.5 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.1 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.1 (64-bit) BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.153.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.153.1001 OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.6.3
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.6.3 PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders
TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders Edraw AIEdraw AI - AI-Powered Visual Collaboration
Edraw AIEdraw AI - AI-Powered Visual Collaboration
Comments and User Reviews