-
Latest Version
Python 3.14.3 (32-bit) LATEST
-
Review by
-
Operating System
Windows 7 / Windows 8 / Windows 10
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
python-3.14.3.exe
Key Features
Readability: Python's syntax emphasizes code readability with its clean and straightforward structure. The use of indentation instead of braces makes the code visually appealing and easy to understand.
Easy to Learn: It has a gentle learning curve, making it an excellent choice for beginners. The simplicity of its syntax allows new programmers to grasp fundamental concepts quickly and start writing functional code.
Large Standard Library: It provides a vast standard library that offers ready-to-use modules for various purposes. It includes modules for string manipulation, file handling, networking, web development, data processing, and much more. Leveraging the standard library saves development time and effort.
Dynamically Typed: It is dynamically typed, meaning that variable types are inferred at runtime. This flexibility allows developers to write code more quickly without explicitly declaring variable types.
Versatility: It can be used for a wide range of applications, including web development, data analysis, scientific computing, artificial intelligence, machine learning, automation, and scripting. Its versatility stems from its extensive library ecosystem, which provides specialized tools and frameworks for different domains.
Cross-platform Compatibility: Python 32bit is available on major operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux, ensuring portability across different environments. The app code written on one platform can typically run on another platform without modification.
Strong Community Support: It has a vibrant and active community of developers worldwide. This community contributes to the language's growth and provides extensive documentation, tutorials, forums, and open-source libraries. The community-driven nature of Python fosters collaboration and continuous improvement.
Python is commonly used in various fields:
Web Development: The web frameworks like Django, Flask, and Pyramid are widely adopted for building scalable and secure web applications.
Data Analysis and Scientific Computing: Python's libraries, such as NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib, enable data manipulation, analysis, and visualization. It is often used in scientific research, data science, and machine learning.
Automation and Scripting: Python's simplicity and ease of use make it a popular choice for automating repetitive tasks, writing scripts, and system administration.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: It offers powerful libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and sci-kit-learn, which are extensively used in developing AI and machine learning models.
Desktop Application Development: It can be used to create cross-platform desktop applications using frameworks like PyQt and Tkinter.
How to Use
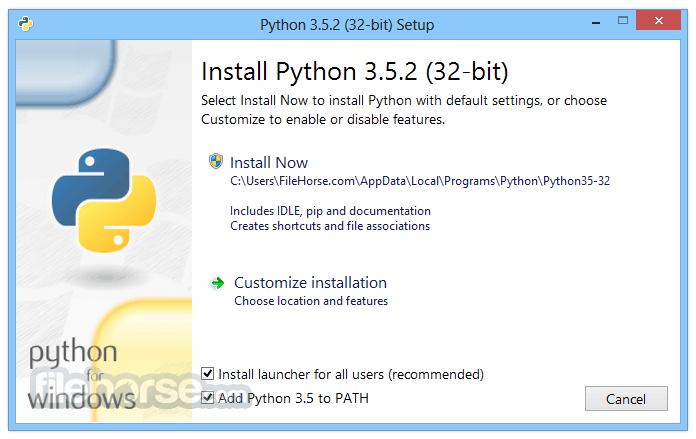
Install Python: Download the installer for your operating system from the official website (python.org) and run it. Follow the installation instructions provided.
Choose a Code Editor or IDE: Select a code editor or Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for writing your Python code. Some popular options include Visual Studio Code, PyCharm, Atom, and Sublime Text. Install your preferred editor/IDE.
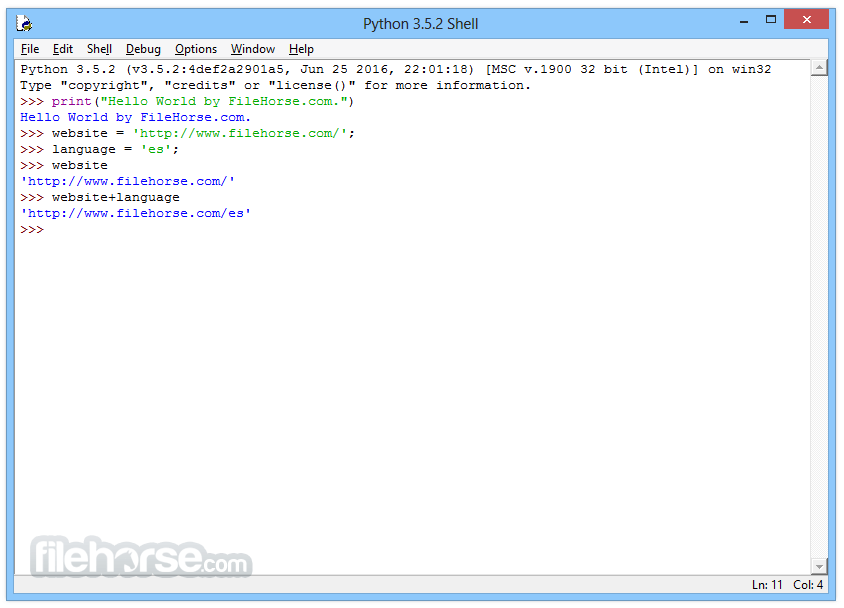
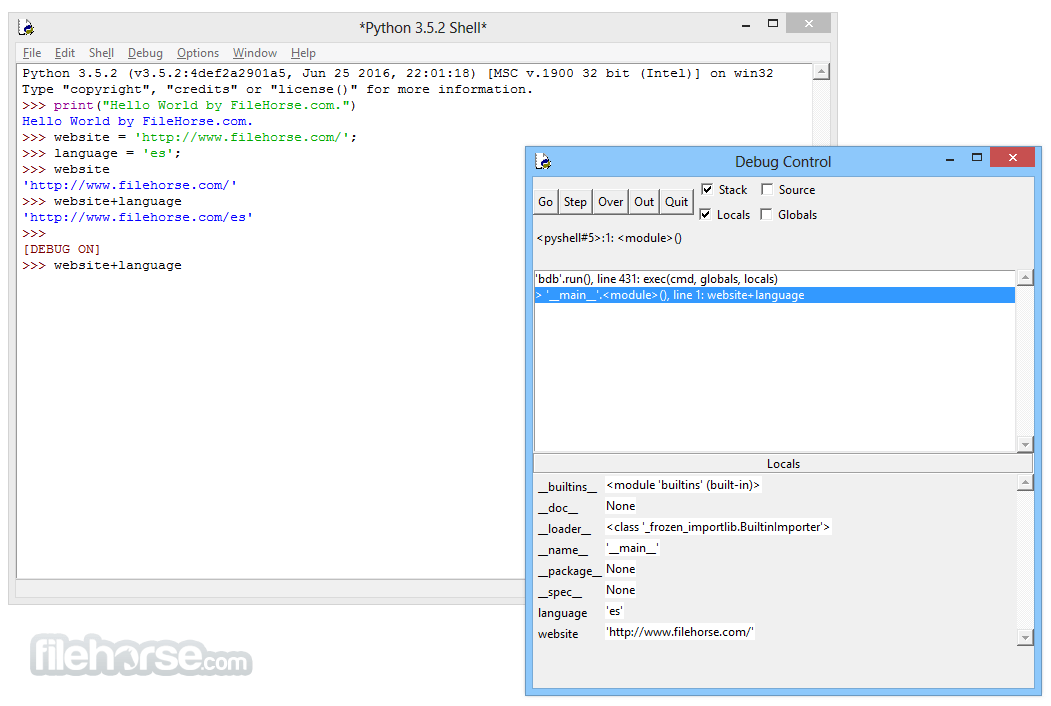
Write Your First Python Program: Open your code editor/IDE and create a new file with a .py extension. This is where you'll write your code. Start by writing a simple program, such as the classic "Hello, World!" program:
print("Hello, World!")
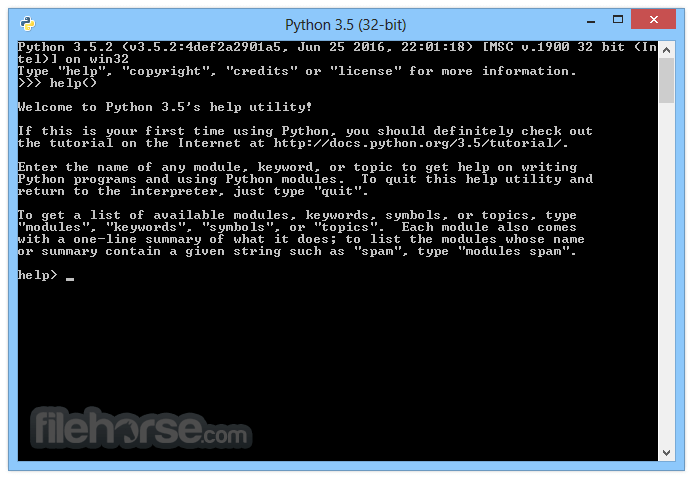
Save and Run Your Program: Save the file with a meaningful name and the .py extension. Open the command prompt or terminal, navigate to the directory where the file is saved, and execute the program using the command:
python filename.py
Learn Python Syntax: Familiarize yourself with Python's syntax and basic concepts. Learn about variables, data types, control flow statements (if-else, loops), functions, and more. Online tutorials, courses, and documentation are excellent resources for learning Python syntax.
Utilize Python Libraries: Python's strength lies in its extensive libraries. Explore libraries relevant to your projects, such as NumPy for numerical computations, Pandas for data manipulation, Matplotlib for data visualization, and TensorFlow or PyTorch for machine learning. Install libraries using the pip package manager:
pip install library_name
Practice and Explore: It offers a wide range of possibilities, so practice coding regularly. Experiment with different functionalities and libraries to expand your knowledge and discover Python's capabilities. Online coding challenges and projects can help you strengthen your skills.
Refer to Documentation and Online Resources: It has comprehensive documentation available on the official website (docs.python.org). It covers the language's syntax, standard libraries, and various topics. Additionally, online communities, forums, and tutorial websites offer valuable resources for learning and problem-solving.
Collaborate and Contribute: Engage with the community by participating in forums, joining local user groups, and contributing to open-source projects. Collaborating with others can enhance your learning experience and allow you to contribute to the growth of the ecosystem.
FAQ
Q: How do I install Python on my PC?
A: To install Python on your PC, visit the official website (python.org) and download the installer for your operating system. Run the installer and follow the instructions provided.
Q: Can I use Python on Windows, macOS, and Linux?
A: Yes, Python is compatible with all major operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. You can write and run Python code on any of these platforms.
Q: What code editor or IDE should I use for Python programming on PC?
A: There are several popular code editors and IDEs available for Python, such as Visual Studio Code, PyCharm, Atom, and Sublime Text. Choose the one that suits your preferences and workflow.
Q: How do I run a Python program on my PC?
A: Save your code with a .py extension. Open the command prompt or terminal, navigate to the directory where the Python file is saved, and run the command "python filename.py" to execute the program.
Q: What are Python packages and how do I install them?
A: Python packages are additional libraries or modules that extend Python's functionality. You can install packages using the pip package manager. For example, to install the NumPy package, run the command "pip install numpy" in the command prompt or terminal.
Q: Can I use Python to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for PC applications?
A: Yes, it provides various GUI frameworks like Tkinter, PyQt, and wxPython that allow you to create desktop applications with graphical interfaces.
Q: Is Python suitable for game development on PC?
A: Yes, it can be used for game development. Libraries like Pygame provide tools and functionality for creating 2D games, while engines like Panda3D and Pyglet offer more advanced capabilities.
Q: Can I use Python for web development on my PC?
A: Absolutely! It has powerful web frameworks like Django and Flask that enable you to build web applications, APIs, and websites using Python on your PC.
Q: Are there resources available for learning Python on PC?
A: Yes, there are numerous resources available for learning Python. You can find online tutorials, documentation, interactive courses, video tutorials, and books that cater to different learning styles and levels of expertise.
Q: Can I contribute to the Python community as a PC user?
A: Definitely! Python is an open-source language with an active community. You can contribute by reporting bugs, suggesting improvements, or even contributing code to the Python core or open-source projects.
Alternatives
JavaScript: Primarily used for web development, JavaScript is a versatile language with an extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. It is particularly suitable for client-side scripting and interactive web applications.
R: A programming language specifically designed for statistical analysis and data visualization. It excels in the field of data science and is preferred by statisticians and researchers.
Java: A general-purpose language known for its robustness, scalability, and cross-platform compatibility. It is widely used for building enterprise-level applications, Android development, and large-scale systems.
Ruby: A dynamic, object-oriented language known for its simplicity and elegant syntax. It is often used in web development frameworks like Ruby on Rails.
System Requirements
- Operating System: Windows, macOS, Linux
- Processor: 1 GHz or faster
- RAM: 1 GB (minimum), 4 GB or more (recommended)
- Disk Space: 200 MB for Python installation
- Simplicity and readability
- Vast library ecosystem
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Extensive community support
- Integration capabilities
- Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) can limit multi-threading performance
- Relatively slower execution speed compared to low-level languages
- Lack of a dedicated GUI (Graphical User Interface)
Overall, Python's versatility, simplicity, extensive library support, and thriving community make it a language that continues to thrive and evolve. Whether you are a beginner exploring programming or an experienced developer seeking a powerful toolset, Python is a language worth considering for its wide range of applications and its ability to facilitate efficient and effective development.
Also Available: Python (64-bit) and Python for Mac
What's new in this version:
New features:
- Free-threaded Python is officially supported
- The evaluation of annotations is now deferred, improving the semantics of using annotations
- Template string literals (t-strings) for custom string processing, using the familiar syntax of f-strings
- Multiple interpreters in the stdlib
- A new module compression.zstd providing support for the Zstandard compression algorithm
- except and except* expressions may now omit the brackets
- Syntax highlighting in PyREPL, and support for color in unittest, argparse, json and calendar CLIs
- A zero-overhead external debugger interface for CPython
- UUID versions 6-8 are now supported by the uuid module, and generation of versions 3-5 are up to 40% faster
- Disallow return/break/continue that exit a finally block
- An improved C API for configuring Python
- A new type of interpreter. For certain newer compilers, this interpreter provides significantly better performance. Opt-in for now, requires building from source.
- Improved error messages.
- Builtin implementation of HMAC with formally verified code from the HACL* project
- A new command-line interface to inspect running Python processes using asynchronous tasks
- The pdb module now supports remote attaching to a running Python process
Build changes:
- Python 3.14 and onwards no longer provides PGP signatures for release artifacts. Instead, Sigstore is recommended for verifiers.
- Official macOS and Windows release binaries include an experimental JIT compiler
- Official Android binary releases are now available
 OperaOpera 127.0 Build 5778.76 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 127.0 Build 5778.76 (64-bit) Kling AIKling AI - Text or Image to Video
Kling AIKling AI - Text or Image to Video PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.3.1 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.3.1 (64-bit) BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.166.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.166.1001 OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum CapCutCapCut 7.9.0
CapCutCapCut 7.9.0 PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2026
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2026 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders
TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders AdGuard VPNAdGuard VPN 2.9.0
AdGuard VPNAdGuard VPN 2.9.0
Comments and User Reviews