-
Latest Version
PostgreSQL 17.4 LATEST
-
Review by
-
Operating System
Windows 7 64 / Windows 8 64 / Windows 10 64 / Windows 11
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
postgresql-17.4-1-windows-x64.exe
It runs on all major operating systems, including Linux, UNIX (AIX, BSD, HP-UX, SGI IRIX, macOS, Solaris, Tru64), and Windows. PostgreSQL is a powerful object-relational database management system! Download PostgreSQL Offline Installer Setup 64bit for PC!
It is fully ACID compliant, has full support for foreign keys, joins, views, triggers, and stored procedures (in multiple languages). It includes most SQL:2008 data types, including INTEGER, NUMERIC, BOOLEAN, CHAR, VARCHAR, DATE, INTERVAL, and TIMESTAMP.
It also supports storage of binary large objects, including pictures, sounds, or video. It has native programming interfaces for C/C++, Java, .Net, Perl, Python, Ruby, Tcl, ODBC, among others, and exceptional documentation (table sizes can go up to 32 TB).
PostgreSQL 2025 comes with many features aimed to help developers build applications, administrators to protect data integrity and build fault-tolerant environments, and help you manage your data no matter how big or small the dataset. In addition to being free and open-source, the tool is highly extensible.
For example, you can define your own data types, build out custom functions, even write code from different programming languages without recompiling your database!
The app tries to conform with the SQL standard where such conformance does not contradict traditional features or could lead to poor architectural decisions.
Many of the features required by the SQL standard are supported, though sometimes with slightly differing syntax or function. Further moves towards conformance can be expected over time.
Features and Highlights
Data Types
- Primitives: Integer, Numeric, String, Boolean
- Structured: Date/Time, Array, Range, UUID
- Document: JSON/JSONB, XML, Key-value (Hstore)
- Geometry: Point, Line, Circle, Polygon
- Customizations: Composite, Custom Types
- UNIQUE, NOT NULL
- Primary Keys
- Foreign Keys
- Exclusion Constraints
- Explicit Locks, Advisory Locks
- Indexing: B-tree, Multicolumn, Expressions, Partial
- Advanced Indexing: GiST, SP-Gist, KNN Gist, GIN, BRIN, Covering indexes, Bloom filters
- Sophisticated query planner/optimizer, index-only scans, multicolumn statistics
- Transactions, Nested Transactions (via savepoints)
- Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC)
- Parallelization of reading queries and building B-tree indexes
- Table partitioning
- All transaction isolation levels defined in the SQL standard, including Serializable
- Just-in-time (JIT) compilation of expressions
- Write-ahead Logging (WAL)
- Replication: Asynchronous, Synchronous, Logical
- Point-in-time-recovery (PITR), active standbys
- Tablespaces
- Authentication: GSSAPI, SSPI, LDAP, SCRAM-SHA-256, Certificate, and more
- Robust access-control system
- Column and row-level security
- Stored functions and procedures
- Procedural Languages: PL/PGSQL, Perl, Python (and many more)
- Foreign data wrappers: connect to other databases or streams with a standard SQL interface
- Many extensions that provide additional functionality, including PostGIS
- Support for international character sets, e.g. through ICU collations
- Full-text search
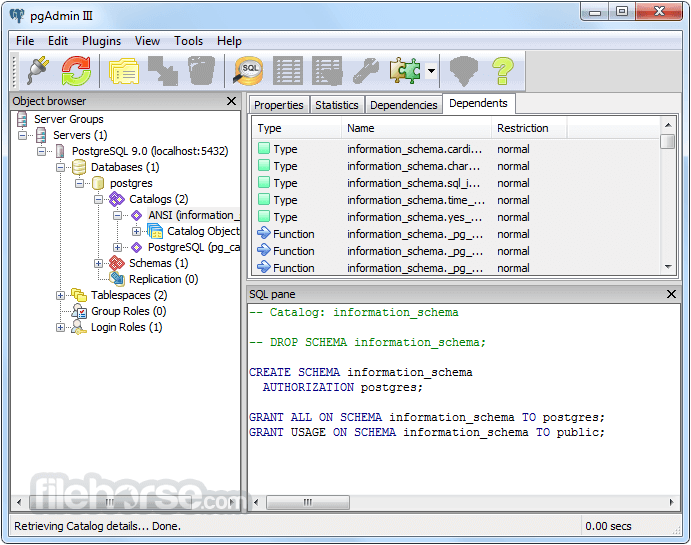
- Download and install this program from the official site or FileHorse.com
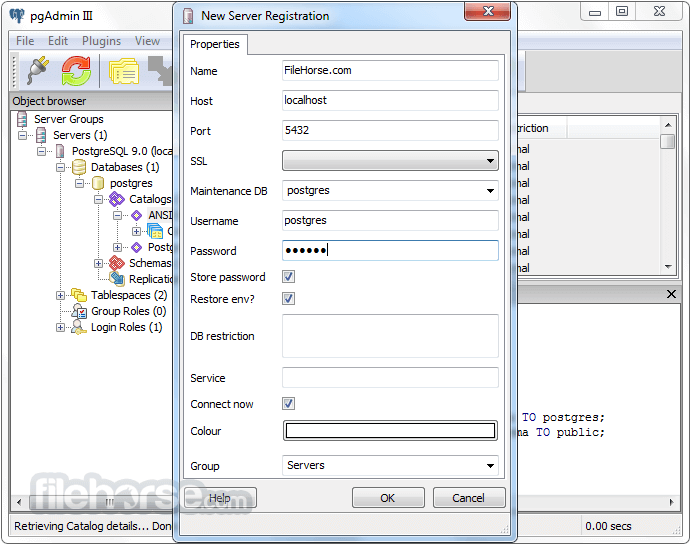
- Open pgAdmin or use the command line for database management
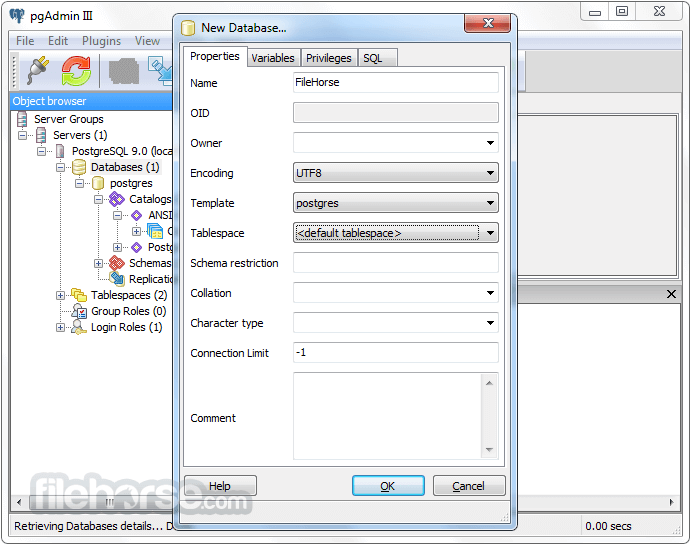
- Create a new database using the pgAdmin interface
- Use SQL queries to create, read, update, and delete data
- Configure user roles and permissions for security
- Backup and restore databases with pgAdmin or command line
- Optimize performance using indexing and query tuning
- Connect applications using PostgreSQL-compatible drivers
- Monitor database activity with built-in logging tools
- Keep PostgreSQL updated for security and performance
OS: Windows 11 or Windows 10 (64-bit)
Processor: Intel or AMD 64-bit processor
RAM: Minimum 2GB, recommended 4GB or more
Storage: At least 100MB for installation, more for data
Additional: Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable required
PROS
- Open-source and free to use
- Advanced security features
- High scalability and performance
- Supports complex queries and indexing
- Strong community and documentation
- Requires manual performance tuning
- Higher memory usage in some cases
- Limited built-in GUI management tools
- Upgrades may require manual adjustments
What's new in this version:
- Improve behavior of libpq's quoting functions
- The changes made for CVE-2025-1094 had one serious oversight: PQescapeLiteral() and PQescapeIdentifier() failed to honor their string length parameter, instead always reading to the input string's trailing null. This resulted in including unwanted text in the output, if the caller intended to truncate the string via the length parameter. With very bad luck it could cause a crash due to reading off the end of memory.
- In addition, modify all these quoting functions so that when invalid encoding is detected, an invalid sequence is substituted for just the first byte of the presumed character, not all of it. This reduces the risk of problems if a calling application performs additional processing on the quoted string.
- Fix small memory leak in pg_createsubscriber
- Fix meson build system to correctly detect availability of the bsd_auth.h system header
 OperaOpera 118.0 Build 5461.41 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 118.0 Build 5461.41 (64-bit) PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.5.0 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.5.0 (64-bit) OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.4.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure
iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.4.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.2.1
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.2.1 BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.51.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.51.1001 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game SemrushSemrush - Keyword Research Tool
SemrushSemrush - Keyword Research Tool LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2
LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2


Comments and User Reviews