-
Latest Version
-
Operating System
Windows XP64 / Vista64 / Windows 7 64 / Windows 8 64 / Windows 10 64
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
mysql-installer-community-5.7.30.0.msi
-
MD5 Checksum
d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
Sometimes latest versions of the software can cause issues when installed on older devices or devices running an older version of the operating system.
Software makers usually fix these issues but it can take them some time. What you can do in the meantime is to download and install an older version of MySQL 5.7.30.
For those interested in downloading the most recent release of MySQL or reading our review, simply click here.
All old versions distributed on our website are completely virus-free and available for download at no cost.
We would love to hear from you
If you have any questions or ideas that you want to share with us - head over to our Contact page and let us know. We value your feedback!
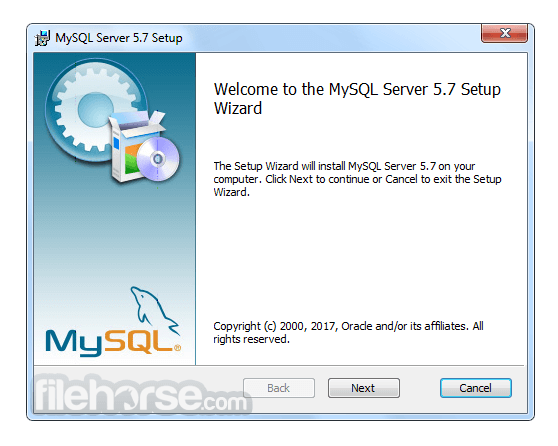
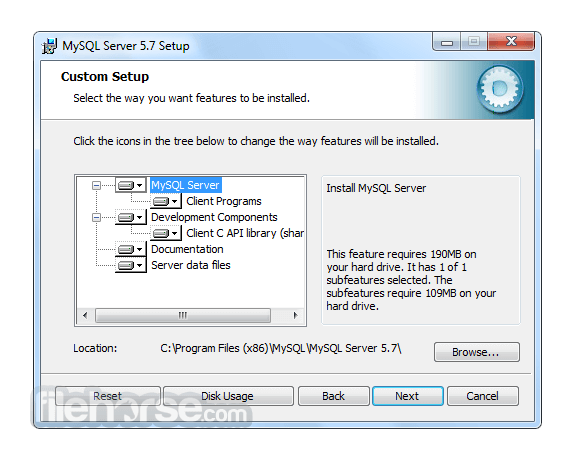
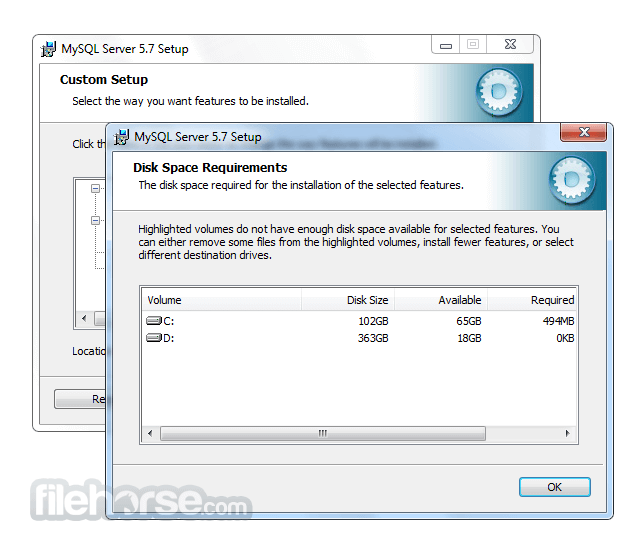
What's new in this version:
JSON Notes:
- The rapidjson library included with MySQL has been upgraded to the GitHub snapshot of 16 January 2020. A fix for a compiler error encountered when building from the snapshot on Mac OS X has been added
Packaging Notes:
- Binary packages that include curl rather than linking to the system curl library have been upgraded to use curl 7.69.0
- The bundled libedit library was upgraded to version 3.1
Bugs Fixed:
- InnoDB: The row_upd_clust_rec_by_insert function, which marks a clustered index record as deleted and inserts an updated version of the record into the clustered index, passed an incorrect n_ext value (the total number of external fields) to lower level functions, causing an assertion failure
- InnoDB: An operation performed with the innodb_buffer_pool_evict debug variable set to uncompressed caused an assertion failure
- InnoDB: An add column operation caused an assertion failure. The failure was due to a dangling pointer
- InnoDB: Updating certain InnoDB system variables that take string values raised invalid read errors during Valgrind testing
- InnoDB: An insert statement on a table with a spatial index raised a record type mismatch assertion due to a tuple corruption
- InnoDB: A function that calculates undo log record size could calculate an incorrect length value in the case of a corrupted undo log record, resulting in a malloc failure. Assertion code was added to detect incorrect calculations
- Replication: While an SQL statement was in the process of being rewritten for the binary log so that sensitive information did not appear in plain text, if a SHOW PROCESSLIST statement was used to inspect the query, the query could become corrupted when it was written to the binary log, causing replication to stop. The process of rewriting the query is now kept private, and the query thread is updated only when rewriting is complete
- Replication: When a GRANT or REVOKE statement is only partially executed, an incident event is logged in the binary log, which makes the replication slave's applier thread stop so that the slave can be reconciled manually with the master. Previously, if a failed GRANT or REVOKE statement was the first statement executed in the session, no GTID was applied to the incident event (because the cache manager did not yet exist for the session), causing an error on the replication slave. Also, no incident event was logged in the situation where a GRANT statement created a user but then failed because the privileges had been specified incorrectly, again causing an error on the replication slave. Both these issues have now been fixed
- Replication: When a replication slave has a generated column that the master does not have in that table, with a secondary index on the generated column, the generated expression should be evaluated and the value stored by the storage engine in the secondary index. When row-based binary logging is in use, the replication slave assigns default values to any fields that are not in the master's definition of the table. In the case of a generated column, which does not have a default value, the slave was previously assigning a null or a zero value to the column. This value was then stored by the storage engine in the secondary index, causing both the table and the index to become corrupted. To fix this issue, generated columns in a table on a replication slave are now re-evaluated before the values are sent to the storage engine
- Replication: In the event of an unplanned disconnection of a replication slave from the master, the reference to the master's dump thread might not be removed from the list of registered slaves, in which case statements that accessed the list of slaves would fail. The issue has now been fixed
- Replication: With the settings binlog_format=MIXED, tx_isolation=READ-COMMITTED, and binlog_row_image=FULL, an INSERT ... SELECT query involving a transactional storage engine omitted any columns with a null value from the row image written to the binary log. This happened because when processing INSERT ... SELECT statements, the columns were marked for inserts before the binary logging format was selected. The issue has now been fixed
- The -libs-compat RPM package is now built with system zlib to avoid problems with unrestricted export of symbols in libmysqlclient.so.18
- The Event Scheduler had a memory leak
- Under certain circumstances, a memcached command could result in reading an uninitialized memory buffer, causing a failure
- Using ALTER USER to reset an account MAX_USER_CONNECTIONS value did not take effect until all current account connections terminated, if there were any
- A materialized subquery including a condition in which a column value was used as input to a nondeterministic function produced incorrect results
- CONCAT() and CONCAT_WS() could produce incorrect results in rare cases due to incorrect substring handling
- Scheduling of events could be disturbed by removing events
- Client programs could load authentication plugins from outside the plugin library
- The server did not handle correctly a UNION in which one of the queries A query with a WHERE clause whose predicate contained a numeric value in scientific notation was not handled correctly.
- In addition, attempting to insert a particular integer specified as a string caused a server exit when the string-to-integer conversion was not successful
- Previously, mysqlpump read the [mysql_dump] and [client] groups from option files. mysqlpump now additionally reads the [mysqlpump] group. The [mysql_dump] group is still accepted but is deprecated
- A multi-table UPDATE statement which updated a table joined to a derived table that joined two other tables was not optimized properly as it had been in MySQL 5.6, instead being treated as if STRAIGHT_JOIN had been used with the subquery creating the derived table
 OperaOpera 125.0 Build 5729.49 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 125.0 Build 5729.49 (64-bit) MalwarebytesMalwarebytes Premium 5.4.5
MalwarebytesMalwarebytes Premium 5.4.5 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.1 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.1 (64-bit) BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.153.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.153.1001 OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.6.3
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.6.3 PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders
TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders Edraw AIEdraw AI - AI-Powered Visual Collaboration
Edraw AIEdraw AI - AI-Powered Visual Collaboration


Comments and User Reviews