-
Latest Version
-
Operating System
Windows XP / Vista / Windows 7 / Windows 8 / Windows 10
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
mysql-5.7.14-win32.msi
-
MD5 Checksum
3abc15eeddc078b0615eb4dcb47cc5d0
Sometimes latest versions of the software can cause issues when installed on older devices or devices running an older version of the operating system.
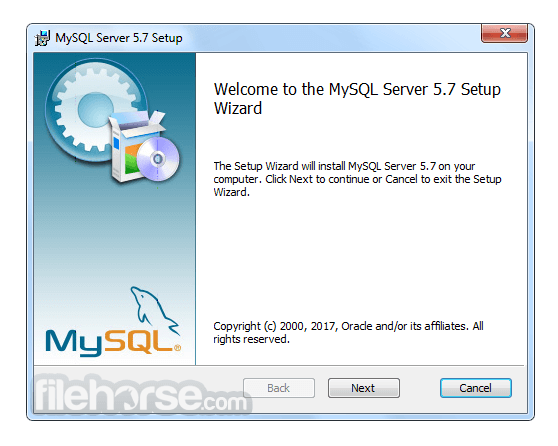
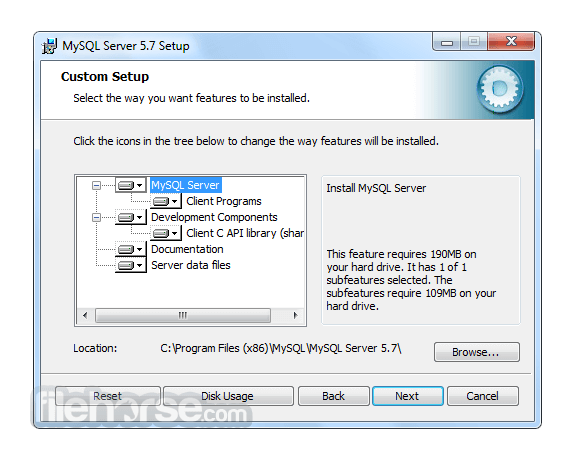
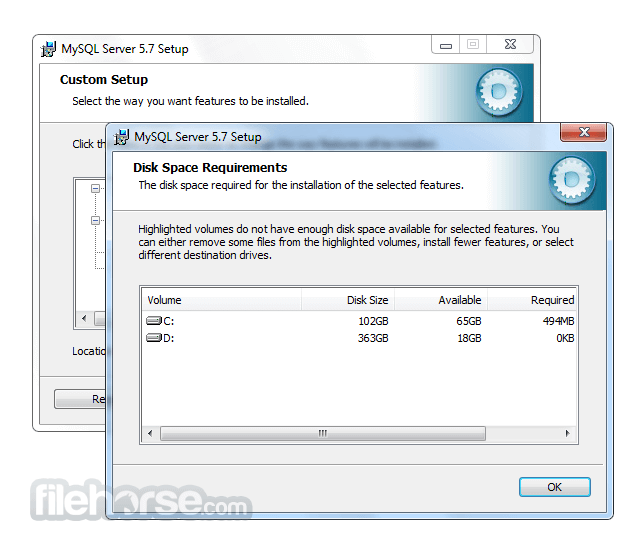
Software makers usually fix these issues but it can take them some time. What you can do in the meantime is to download and install an older version of MySQL 5.7.14 (32-bit).
For those interested in downloading the most recent release of MySQL or reading our review, simply click here.
All old versions distributed on our website are completely virus-free and available for download at no cost.
We would love to hear from you
If you have any questions or ideas that you want to share with us - head over to our Contact page and let us know. We value your feedback!
What's new in this version:
SYS SCHEMA NOTES:
- The sys schema now has a quote_identifier() function that, given a string argument, produces a quoted identifier suitable for inclusion in SQL statements. (Bug #22011361, Bug #78823)
- Output from the sys schema diagnostics() procedure now includes the Tls_version column from the mysql.slave_master_info system table.
FUNCTIONALITY ADDED OR CHANGED:
- The %global compatver value for RPM packages for RHEL/OEL and Fedora releases was updated from 5.6.25 to 5.6.31. (Bug #23038018)
- Specifying an empty value for the --port option (for example, --port=, --port="") is now deprecated and results in a warning. An empty value will be an error in MySQL 8.0. (Bug #23023457, Bug #80903)
- CMake support for compiling with Solaris Studio 12.5 was added. (Bug #82249, Bug #24303829, Bug #81274, Bug #23212938)
- The INFORMATION_SCHEMA INNODB_LOCKS and INNODB_LOCK_WAITS tables are now deprecated and will be removed in a future MySQL release.
BUGS FIXED:
- Performance: A flaw in the allocation of memory for appending string values caused some operations to be performed slowly, including creation of tables having generated columns and inserts of large values into JSON columns. (Bug #80556, Bug #22843444)
- InnoDB: Full-text search auxiliary tables could be dropped by one session while being access by another. (Bug #23742339)
- InnoDB: Selecting full-text index information schema tables for a deleted table caused a segmentation fault. (Bug #23479595)
- InnoDB: A tablespace operation did not properly update the SYS_VIRTUAL system table. (Bug #23325659)
- InnoDB: Rollback of a full-text index synchronization operation raised an assertion. The rollback operation attempted to acquire a mutex still held by the background synchronization thread. (Bug #23320569)
- InnoDB: After compressing a table, an incorrect data length was passed to an internal tablespace encryption function, causing an assertion. (Bug #23279788)
- InnoDB: An r-tree page lock placed during a search operation prevented an undo operation within the same transaction from merging pages. (Bug #23241575)
- InnoDB: A bulk load insert of a record with a compressed size greater than half of the compressed page size resulted in infinite B-tree page splitting when compressing the uncompressed page. (Bug #23120933)
- InnoDB: A lock order violation related to InnoDB full-text search caused errors and raised an assertion. (Bug #23120005)
- InnoDB: In read-only mode, InnoDB attempted to set a corrupt bit in the SYS_INDEXES system table. In read-only mode, the corruption should only be marked in memory. (Bug #23077748)
- InnoDB: InnoDB attempted to materialize non-key generated virtual columns that were not required for partitioning. (Bug #23037025)
- InnoDB: An insert operation on a table containing virtual and spatial indexes raised an assertion due to an invalid parent path encountered during page splitting. (Bug #23008863)
- InnoDB: An ALTER TABLE operation on a table with an indexed virtual column raised an assertion. (Bug #22965271)
- InnoDB: Adding or dropping a generated virtual column could raise an assertion due to a table handle held by an active memcached connection. (Bug #22922527)
- InnoDB: A full-text query that involved a large number of records exceeded the result cache limit and caused a server exit. (Bug #22709692, Bug #80296)
- InnoDB: InnoDB did not block the creation of a foreign key constraint with referential actions on the base column of a generated stored column. (Bug #22687023, Bug #80304)
- InnoDB: The optimizer failed to mark the columns required for MATCH function evaluation when the secondary index used for the full-text query was not chosen by the optimizer. (Bug #22679209, Bug #80298)
- InnoDB: In READ COMMITTED isolation level, InnoDB unnecessarily acquired the lock_sys mutex at COMMIT for a transaction block consisting of read-only SELECT statements.
- InnoDB: Setting innodb_monitor_enable to all did not enable all counters. (Bug #22576241, Bug #80083)
- InnoDB: InnoDB now permits defining a foreign key constraint with a cascading referential action on the base column of an indexed virtual column, and defining cascading referential actions on non-virtual foreign key columns that are explicitly included in a virtual index. (Bug #22469130, Bug #79772)
- InnoDB: An assertion was raised during rollback of an ALTER TABLE operation that dropped and added a secondary index. (Bug #22005726)
- Partitioning: In some cases, an issue with partition pruning being attempted a second time during optimization after all partitions had already been pruned at parsing time led to an assert. (Bug #23194259)
- Replication: Replication slaves could exit trying to apply an UPDATE row event containing virtual generated columns received from a master that was set to binlog_row_image=minimal. (Bug #23604483)
- Replication: When using row-based replication and InnoDB, replication slaves reverted to using an older locking scheme when a transaction had already acquired an AUTOINC lock related to a LOAD FILE or INSERT ... SELECT type of statement, reducing replication slave performance. The fix ensures that sql_command is set correctly for any of the DML events such as WRITE_ROWS_EVENT, UPDATE_EVENT, and DELETE_EVENT. (Bug #79324, Bug #22247668)
- Replication: When using statement-based or mixed binary logging format with --read-only=ON, it was not possible to modify temporary tables. (Bug #62008, Bug #12818255)
- References: See also: Bug #14294223, Bug #16561483.
- MySQL Server upgrades performed using RPM packages failed when upgrading from MySQL 5.6 Community to MySQL 5.7 Community or MySQL 5.6 Commercial to MySQL 5.7 Commercial. (Bug #23736787)
- On CentOS, mysqld installed from a MySQL Community distribution failed to start if a my.cnf file with no datadir value specified was used. (Bug #23721277, Bug #82049)
- The -DWITH_EDITLINE=system CMake option failed with recent versions of the editline library. (Bug #23708332)
- Executing prepared statements with the audit_log plugin installed could cause a server exit. (Bug #23699991)
- The sys schema ps_trace_statement_digest() procedure failed for statements not supported by EXPLAIN, for statements for which EXPLAIN could not find tables, and for statements with no digest found during the monitored period. (Bug #23621189)
- A SELECT Performance Schema tables when an internal buffer was full could cause a server exit. (Bug #23550835, Bug #23298025, Bug #81464)
- The code for reading character set information from Performance Schema statement events tables (for example, events_statements_current) did not prevent simultaneous writing to that information. As a result, the SQL query text character set could be invalid, which could result in a server exit. Now an invalid character set causes SQL_TEXT column truncation. (Bug #23540008)
- An error message spelling error was corrected. Thanks to Derek Jones for the patch. (Bug #23525874, Bug #81713)
- In the Performance Schema, allocating a record when a buffer was full could lead to a server exit. (Bug #23515302)
- A buffer overflow in the regex library was fixed. (Bug #23498283)
- Upgrading from native MySQL 5.6 Debian/Ubuntu packages to Oracle-supplied MySQL 5.7 packages caused server restart failures. (Bug #23498230)
- The CMake configuration was too aggressive in making symbols invisible, resulting in link problems with GCC 5.3 on Solaris. (Bug #23344916, Bug #81593)
- Audit log filtering against the user was performing comparisons against USER(), not CURRENT_USER(). (Bug #23344762)
- After upgrading only the server using RPM packages, the server could fail to start, complaining about a bad errmsg.sys file. (Bug #23338603)
- Upgrading from native Ubuntu 5.7.12 packages to MySQL 5.7.13 packages failed with conflict messages. (Bug #23327563)
- For debug builds, the server exited abnormally if a shutdown command was issued while the audit_log plugin was loaded and an active connection existed. (Bug #23310864)
- The server could fail to interpret expired passwords as expired. (Bug #23291841)
- Certain arguments to NAME_CONST() could cause a server exit. (Bug #23279858)
- For unit-testing with the MySQL test suite, the make unit-test command is no longer available. The ctest program should be used instead. See Unit Tests Added to Main Test Runs. (Bug #23273434)
- Audit log plugins (including query rewrite plugins, which use the audit API) were being acquired and released per statement, negatively affecting scalability. To improve performance, these plugins now are acquired once and released only when the connection ends. (Bug #23236404, Bug #81298)
- mysql-test-run.pl now has a --manual-boot-gdb option that is similar to --boot-gdb but attaches the debugger to the server during the bootstrapping process, permitting the use of a remote debugger. (Bug #23090633)
- The -fexpensive-optimizations option to GCC caused ARM64 and PowerPC builds to compute floating-point operations slightly differently from other platforms. CMake now checks for this problem and disables the option as necessary. (Bug #23046775)
- The test_service_sql_api.test_session_general_log test case now cleans up the general_log table by truncating it at the end of the test. Thanks to Daniel Black for the patch. (Bug #23021111, Bug #80895)
- Lines written to the error log had no space separating the timestamp and thread ID columns if the thread ID took five or more characters. (Bug #23005009, Bug #80854)
- For the innodb_buffer_stats_by_schema and innodb_buffer_stats_by_table sys schema views, the pages_hashed and pages_old columns were incorrect. Thanks to Tsubasa Tanaka for the patch. (Bug #22988461, Bug #80833)
- An incorrect result could be returned for a query using a merged derived table or a view when compared to a similar query using a base table directly, if the query included a WHERE condition in a scalar subquery inside a HAVING condition of the main query block. (Bug #22967439)
- ST_GeomFromGeoJSON() treated JSON NULL as invalid input. Now it treats JSON NULL as SQL NULL and thus returns SQL NULL for JSON NULL input. (Bug #22930020, Bug #80712)
- For the host_summary_by_statement_latency and x$host_summary_by_statement_latency sys schema views, the max_latency column was incorrect. (Bug #22848110, Bug #80569)
- ST_Distance() could raise an assertion for NULL return values. (Bug #22760390)
- In the absence of SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS, FOUND_ROWS() for a UNION statement always returned the actual number of rows found even when LIMIT was present. (Bug #22602381, Bug #80148)
- A statement containing a format specifier resulted in a server exit when the query rewrite plugin tried to log the statement. (Bug #22601485)
- With the query cache enabled, executing a prepared statement with CURSOR_TYPE_READ_ONLY and then again with CURSOR_TYPE_NO_CURSOR caused the server to return an error. (Bug #22559575, Bug #80026)
- mysql_real_connect() was not thread-safe when invoked with the MYSQL_READ_DEFAULT_FILE or MYSQL_READ_DEFAULT_GROUP option enabled. (Bug #22322504, Bug #79510)
- With GTIDs enabled, XA COMMIT on a disconnected XA transaction within a multiple-statement transaction raised an assertion. (Bug #22173903)
- The sys schema create_synonym_db() function failed if the synonym name was a reserved word or contained backtick (`) characters. (Bug #22011361, Bug #78823)
- The sys schema host_summary view could fail with a division-by-zero error. (Bug #21970078)
- The GCC workaround for compiling on ARM64 added by Bug #21552524 is needed only for GCC before 5.2.1. (Bug #21845828)
- The sys schema format_path() function replaced substrings of the path name argument without verifying that the substrings were delimited by path name separators. Replacement now works correctly, including on Windows. A consequence is that backslashes in Windows path names are no longer converted to forward slashes in the result. (Bug #21512106)
- MySQL now supports compiling using the GCC __atomic builtins introduced in GCC 4.7 that permit a more efficient implementation of the MySQL atomics API. These __atomic builtins are only used for platforms where the old GCC __sync builtins are not available, such as PowerPC where the server otherwise would not build. (Bug #21221500)
- If a stored function updated a view for which the view table had a trigger defined that updated another table, it could fail and report an error that an existing table did not exist. (Bug #21142859, Bug #76808)
- mysql_upgrade failed to upgrade the sys schema if a sys database directory existed but was empty. (Bug #81352, Bug #23249846, Bug #22875519)
- The bundled Protobuf sources (under the extra directory) were upgraded from version 2.6.0 to 2.6.1. (Bug #81280, Bug #23213376)
- Protobuf is currently used only by the X plugin, but MySQL builds built the protobuf libraries and executables even if X plugin building was disabled with -DWITH_RAPID=0. (Bug #81066, Bug #23097750)
- On Solaris, a misaligned memory buffer could cause a server exit when selecting from the global_status Performance Schema table. (Bug #81065, Bug #23097305)
- A compilation error was corrected for a make_link() call when compiling in C++11 mode. Thanks for Daniel Black for the contribution. (Bug #80996, Bug #23080289)
- Two mysql-test-run.pl tests (ctype_gb18030_binlog and ctype_ldml) failed to produce repeatable output due to improper cleanup. Thanks to Daniel Black for the patch. (Bug #80896, Bug #23021095)
- MySQL failed to build with GCC 6 using the default mode for C++ of -std=gnu++14. The CMake configuration has been adjusted to explicitly set the mode to -std=gnu++03 for GCC 6. (Bug #80371, Bug #22732697)
- Ubuntu packages create the root user account using the auth_socket authentication plugin to achieve secure-by-default installation if installation was done with a blank root password. However, auth_socket was being used even if the password was not blank. (Bug #80137, Bug #22594846, Bug #23321113, Bug #81518)
- Compiling the InnoDB memcached plugin did not work on some platforms where MySQL was configured using -DWITH_LIBEVENT=system. (Bug #80073, Bug #22573379, Bug #23567441)
- The client-side plugin deinitialization function signature was changed from int (*deinit)() to int (*deinit)(void) to avoid warnings when compiling with -Wstrict-prototypes. (Bug #78177, Bug #21680094, Bug #81419, Bug #23282498)
- Several issues were addressed in the sys schema stored procedures that show enabled or disabled Performance
Schema setup:
- Enabled and disabled accounts were shown as host@user, not user@host.
- Disabled users in ps_setup_show_disabled were called enabled_users.
- ps_setup_show_enabled() showed disabled objects.
- setup_actors content was not filtered (all rows were returned whether the actor was enabled or disabled).
- Output order is more deterministic.
 OperaOpera 117.0 Build 5408.35 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 117.0 Build 5408.35 (64-bit) PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.3 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.3 (64-bit) OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.3.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure
iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.3.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.1
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.1 BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.41.661.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.41.661.1001 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders
TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2
LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2


Comments and User Reviews