-
Latest Version
-
Operating System
Windows XP / Vista / Windows 7 / Windows 8 / Windows 10
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
mysql-5.5.48-win32.msi
-
MD5 Checksum
2de6a9a3dff76c9b748c7312fd64adb9
Sometimes latest versions of the software can cause issues when installed on older devices or devices running an older version of the operating system.
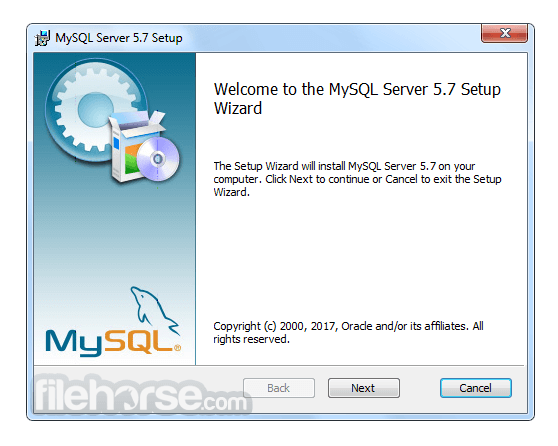
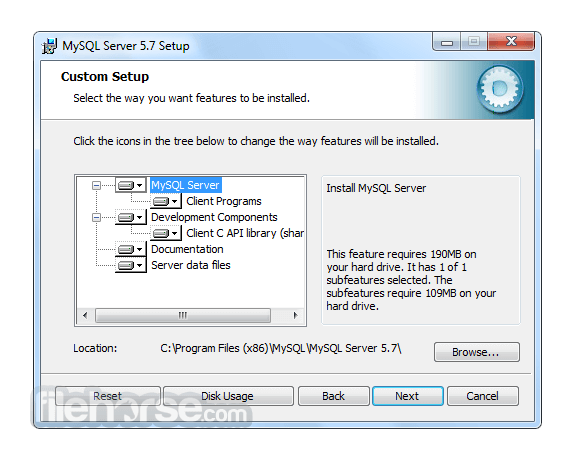
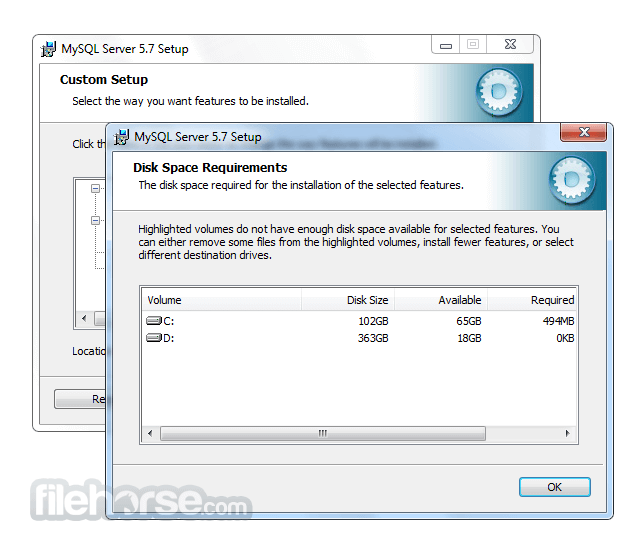
Software makers usually fix these issues but it can take them some time. What you can do in the meantime is to download and install an older version of MySQL 5.5.48 (32-bit).
For those interested in downloading the most recent release of MySQL or reading our review, simply click here.
All old versions distributed on our website are completely virus-free and available for download at no cost.
We would love to hear from you
If you have any questions or ideas that you want to share with us - head over to our Contact page and let us know. We value your feedback!
What's new in this version:
Bug Fixed:
- Replication: When DML invokes a trigger or a stored function that inserts into an AUTO_INCREMENT column, that DML has to be marked as an unsafe statement. If the tables are locked in the transaction prior to the DML statement (for example by using LOCK TABLES), then the DML statement was not being marked as an unsafe statement. The fix ensures that such DML statements are marked correctly as unsafe
- Replication: DROP TABLE statements are regenerated by the server before being written to the binary log. If a table or database name contained a non-regular character, such as non-latin characters, the regenerated statement was using the wrong name, breaking replication. The fix ensures that in such a case the regenerated name is correctly converted back to the original character set. Also during work on this bug, it was discovered that in the rare case that a table or database name contained 64 characters, the server was throwing an assert(M_TBLLEN < 128) assertion. The assertion has been corrected to be less than or equal 128
- Data corruption or a server exit could occur if a stored procedure had a variable declared as TEXT or BLOB and data was copied to that variable using SELECT ... INTO syntax from a TEXT or BLOB column
- CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE .. SELECT statements involving BIT columns that resulted in a column type redefinition could cause a server exit or an improperly created table
- Added Microsoft Visual Studio 2015 support. Changes include using the native (added in VS 2015) timespec library if it exists, renamed lfind/lsearch and timezone/tzname to avoid redefinition problems, set TMPDIR to "" by default as P_tmpdir no longer exists, deprecated std::hash_map in favor of std::unordered_map, and added Wix Toolset 3.10 support
- When an invalid date was supplied to the UNIX_TIMESTAMP() function using the STR_TO_DATE() function, no check was performed before converting it to a timestamp value
- With LOCK TABLES in force, an attempt to open a temporary MERGE table consisting of a view in its list of tables (not the last table in the list) caused a server exit
- For certain prepared statements, the optimizer could transform join conditions such that it used a pointer to a temporary table field that was no longer available after the initial execution. Subsequent executions caused a server exit
- Repeated execution of ALTER TABLE v1 CHECK PARTITION as a prepared statement, where v1 is a view, led to a server exit
- In addition, output for some administrative operations, when they are attempted on a view, changes from “Corrupt” to “Operation failed”. These include ANALYZE TABLE, OPTIMIZE TABLE, and REPAIR TABLE, and ALTER TABLE statements that perform ANALYZE PARTITION, CHECK PARTITION, OPTIMIZE PARTITION, and REPAIR PARTITION operations
- Using systemd to start mysqld failed if configuration files contained multiple datadir lines. Now the last datadir line is used
 OperaOpera 117.0 Build 5408.197 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 117.0 Build 5408.197 (64-bit) PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.5.0 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.5.0 (64-bit) OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.4.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure
iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.4.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.2.1
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.2.1 BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.50.1004
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.50.1004 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game SemrushSemrush - Keyword Research Tool
SemrushSemrush - Keyword Research Tool LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2
LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2


Comments and User Reviews