-
Latest Version
-
Operating System
Windows XP64 / Vista64 / Windows 7 64 / Windows 8 64
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
mysql-5.5.39-winx64.msi
-
MD5 Checksum
c54d81549cc0054d547525010a131f13
Sometimes latest versions of the software can cause issues when installed on older devices or devices running an older version of the operating system.
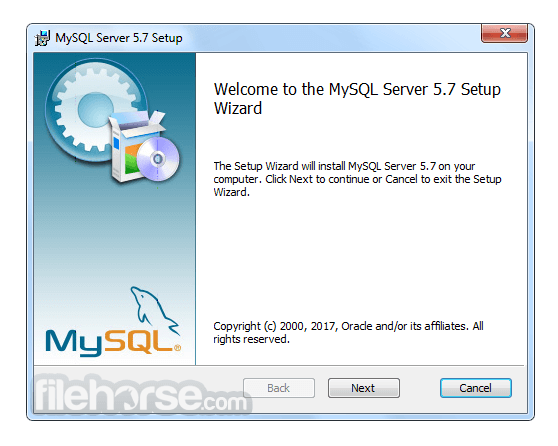
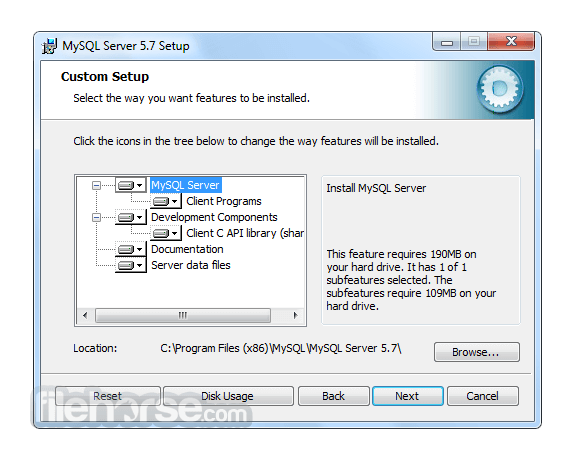
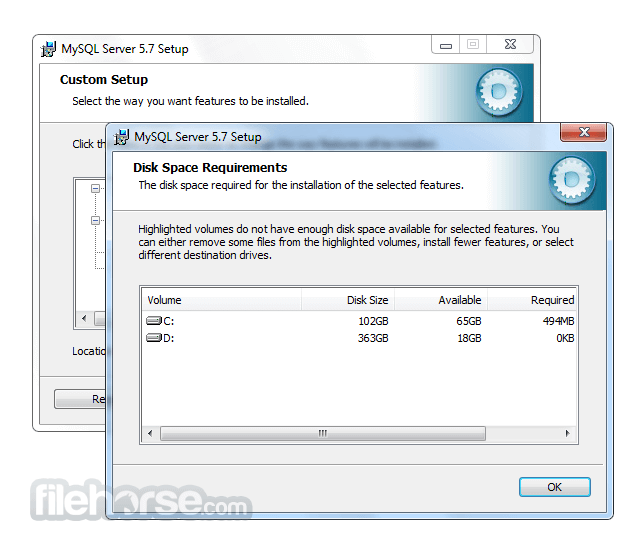
Software makers usually fix these issues but it can take them some time. What you can do in the meantime is to download and install an older version of MySQL 5.5.39 (64-bit).
For those interested in downloading the most recent release of MySQL or reading our review, simply click here.
All old versions distributed on our website are completely virus-free and available for download at no cost.
We would love to hear from you
If you have any questions or ideas that you want to share with us - head over to our Contact page and let us know. We value your feedback!
What's new in this version:
Functionality Added or Changed:
- CMake support was updated to handle CMake version 3.
- The timed_mutexes system variable has no effect and is deprecated. Bugs Fixed:
- InnoDB: Opening a parent table that has thousands of child tables could result in a long semaphore wait condition.
- Partitioning: Selecting from a table having multiple columns in its primary key and partitioned by LIST COLUMNS(R), where R was the last (rightmost) column listed in the primary key definition, returned an incorrect result.
- Replication: When using row-based replication, updating or deleting a row on the master that did not exist on the slave led to failure of the slave when it tried to process the change. This problem occurred with InnoDB tables lacking a primary key.
- Replication: Quotation marks were not always handled correctly by LOAD DATA INFILE when written into the binary log.
- Replication: A group of threads involved in acquiring locks could deadlock when the following events occurred:
> Dump thread reconnects from slave; on master, a new dump thread tries to kill zombie dump threads; having acquired the thread's LOCK_thd_data, it is about to acquire LOCK_log.
> Application thread executing show binary logs, having acquired LOCK_log and about to acquire LOCK_index.
> Application thread executing PURGE BINARY LOGS; having acquired LOCK_index, it is about to acquire LOCK_thread_count.
> Application thread executing SHOW PROCESSLIST (or SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROCESSLIST), having acquired LOCK_thread_count and about to acquire the zombie dump thread's LOCK_thd_data.
- SHA and MD5 functions failed for operations using the internal filename character set and could cause a server exit.
- Large arguments passed to mysqldump could lead to buffer overflow and program exit.
- Compiler flags were not passed to DTrace, causing problems for 32-bit builds cross-compiled on 64-bit platforms.
- ALTER TABLE on a partitioned table could result in the wrong storage engine being written into the table's .frm file and displayed in SHOW CREATE TABLE.
- With the max_heap_table_size system variable set to a large value (20GB), creation of a temporary table or a table using the MEMORY storage engine caused a server exit.
- mysqladmin password masked the old password given on the command line, but not the new password.
- yaSSL code had an off-by-one error in certificate decoding that could cause buffer overflow.
- yaSSL code had an opendir() without a corresponding closedir().
- MyISAM temporary files could be used to mount a code-execution attack.
- If a query had both MIN()/MAX() and aggregate_function(DISTINCT) (for example, SUM(DISTINCT)) and was executed using Loose Index Scan, the result values of MIN()/MAX() were set improperly.
- For UNION statements, the rows-examined value was calculated incorrectly. This was manifest as too-large values for the ROWS_EXAMINED column of Performance Schema statement tables (such as events_statements_current).
- Clients could determine based on connection error message content whether an account existed.
- An assertion could be raised when creating a index on a prefix of a TINYBLOB or GEOMETRY column in an InnoDB column.
- Use of a nonmultibyte algorithm for skipping leading spaces in multibyte strings could cause a server exit.
- For a view defined on a UNION, the server could create an invalid view definition.
- Deadlock could occur if three threads simultaneously performed INSTALL PLUGIN, SHOW VARIABLES, and mysql_change_user().
- MySQL did not compile with Bison 3. A workaround is to downgrade to Bison 2.
- Uninstalling and reinstalling semisynchronous replication plugins while semisynchronous replication was active caused replication failures. The plugins now check whether they can be uninstalled and produce an error if semisynchronous replication is active. To uninstall the master-side plugin, there must be no semisynchronous slaves. To uninstall the slave-side plugin, there must be no semisynchronous I/O threads running.
- If there was a predicate on a column referenced by MIN() or MAX() and that predicate was not present in all the disjunctions on key parts earlier in the compound index, Loose Index Scan returned an incorrect result.
- File permissions and line endings of several test and configuration files were made more consistent to avoid warnings from package checkers.
 OperaOpera 117.0 Build 5408.39 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 117.0 Build 5408.39 (64-bit) PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.4 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.4 (64-bit) OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.3.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure
iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.3.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.1
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.1 BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.41.661.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.41.661.1001 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders
TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2
LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2


Comments and User Reviews