-
Latest Version
-
Operating System
Windows XP64 / Vista64 / Windows 7 64 / Windows 8 64
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
mysql-5.5.38-winx64.msi
-
MD5 Checksum
9819754453d2344938134b3a3ddd277c
Sometimes latest versions of the software can cause issues when installed on older devices or devices running an older version of the operating system.
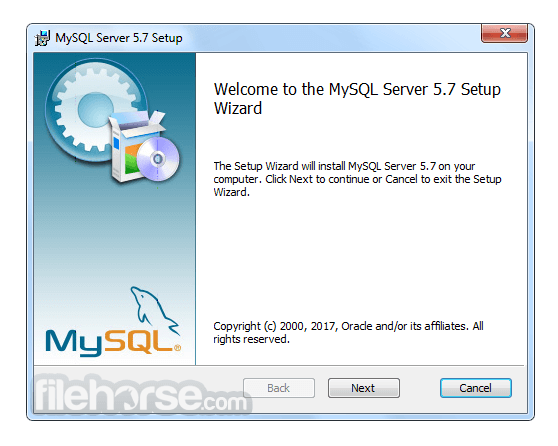
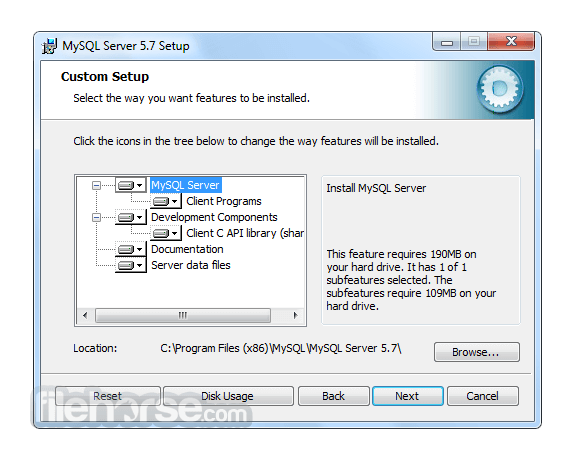
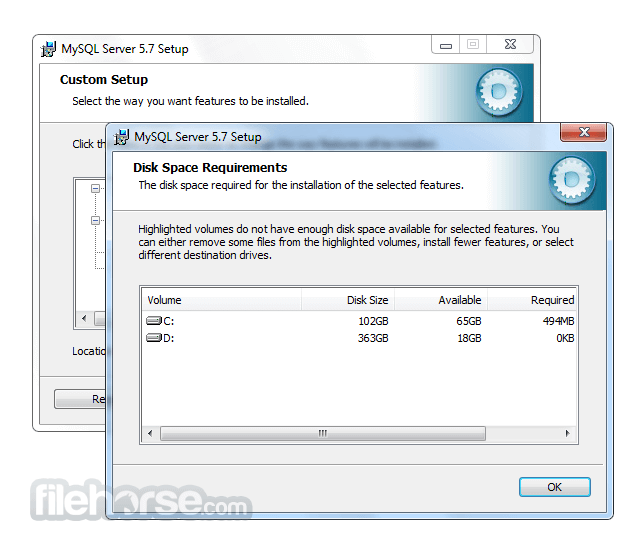
Software makers usually fix these issues but it can take them some time. What you can do in the meantime is to download and install an older version of MySQL 5.5.38 (64-bit).
For those interested in downloading the most recent release of MySQL or reading our review, simply click here.
All old versions distributed on our website are completely virus-free and available for download at no cost.
We would love to hear from you
If you have any questions or ideas that you want to share with us - head over to our Contact page and let us know. We value your feedback!
What's new in this version:
Bugs Fixed:
- InnoDB: For each insert, memset would be called three times to allocate memory for system fields. To reduce CPU usage, the three memset calls are now combined into a single call.
- Replication: When used on a table employing a transactional storage engine, a failed TRUNCATE TABLE was still written to the binary log and thus replayed on the slave. This could lead to inconsistency when the master retained data that was removed on the slave. Now in such cases TRUNCATE TABLE is logged only when it executes successfully.
- Certain INFORMATION_SCHEMA queries could cause a server exit.
- For indexes on prefixes or character string columns, index corruption could occur for assignment of binary data to the column due to improper character counting.
- Solaris-specific scripts were included in and installed by non-Solaris packages.
- EXPLAIN on a query with an EXISTS subquery containing a UNION could cause a server exit. Multiple executions of a prepared EXPLAIN on a UNION of subqueries could cause a server exit.
- Executing a correlated subquery on an ARCHIVE table which has an AUTO_INCREMENT column caused the server to hang.
- The client library could cause clients to exit due to incorrectly mapping the client error number to the corresponding message, if reallocation of packet buffer memory occurred.
- Calling mysql_get_server_version() with an invalid connection handler argument caused the client to exit. Now it returns 0 and reports a CR_COMMANDS_OUT_OF_SYNC error.
- On Windows, calling mysql_thread_init() call without mysql_init() caused the client to exit. windows. Now it returns a nonzero result because it is an error to call mysql_thread_init() before the client library is initialized with mysql_library_init().
- CMake produced not-useful warnings about INTERFACE_LINK_LIBRARIES policy.
- LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE could use all CPU if import errors occurred when there were no line delimiters.
- A statement of the following form broke row-based replication because it created a table having a field of data type BIGINT with a display width of 3000, which is beyond the maximum acceptable value of 255: CREATE TABLE t1 AS SELECT REPEAT('A',1000) DIV 1 AS a;
 OperaOpera 126.0 Build 5750.43 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 126.0 Build 5750.43 (64-bit) MalwarebytesMalwarebytes Premium 5.4.6
MalwarebytesMalwarebytes Premium 5.4.6 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.2 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.2 (64-bit) BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.160.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.160.1001 OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.6.3
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.6.3 PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders
TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders WPS OfficeWPS Office Free 12.2.0.23155
WPS OfficeWPS Office Free 12.2.0.23155


Comments and User Reviews