-
Latest Version
-
Operating System
Windows XP / Vista / Windows 7
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
mysql-5.5.25-win32.msi
-
MD5 Checksum
30bbe7de6cc4d45399da6037689d67e6
Sometimes latest versions of the software can cause issues when installed on older devices or devices running an older version of the operating system.
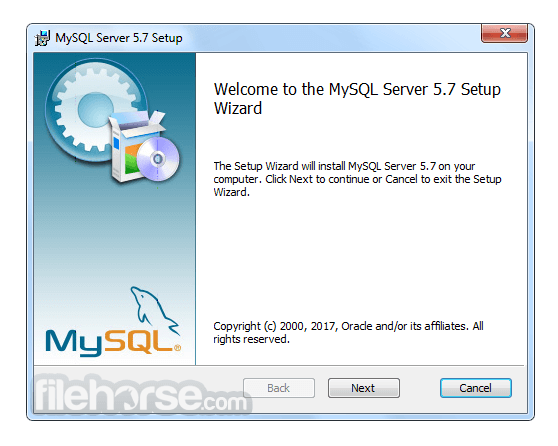
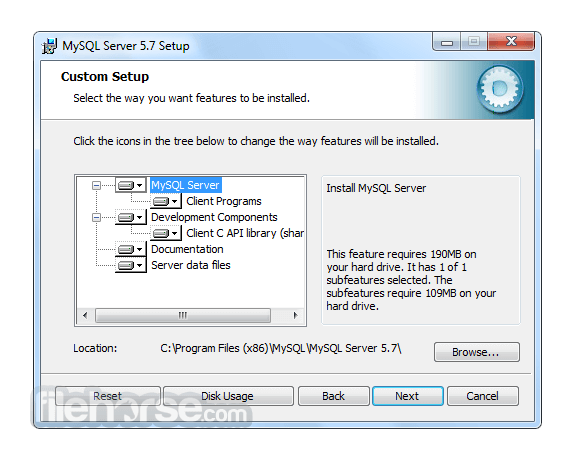
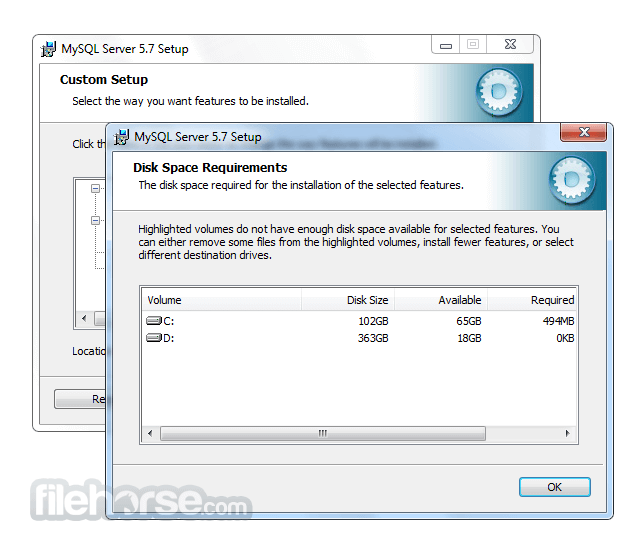
Software makers usually fix these issues but it can take them some time. What you can do in the meantime is to download and install an older version of MySQL 5.5.25 (32-bit).
For those interested in downloading the most recent release of MySQL or reading our review, simply click here.
All old versions distributed on our website are completely virus-free and available for download at no cost.
We would love to hear from you
If you have any questions or ideas that you want to share with us - head over to our Contact page and let us know. We value your feedback!
What's new in this version:
Functionality Added or Changed:
- The --safe-mode server option now is deprecated and will be removed in MySQL 5.6.
Bugs Fixed:
- Performance: InnoDB: Improved the algorithm related to adaptive flushing. This fix increases the rate of flushing in cases where compression is used and the data set is larger than the buffer pool, leading to eviction.
- InnoDB: In a transaction using the REPEATABLE READ isolation level, an UPDATE or DELETE statement for an InnoDB table could sometimes overlook rows recently committed by other transactions. As explained in Section 14.3.9.2, “Consistent Nonlocking Reads”, DML statements within a REPEATABLE READ transaction apply to rows committed by other transactions, even if a query could not see those rows.
- InnoDB: The Innodb_buffer_pool_pages_flushed status variable was incorrectly set to twice the value it should be. Its value should never exceed the value of Innodb_pages_written.
- InnoDB: The error handling and message was improved for attempting to create a foreign key with a column referencing itself. The message suggested a potential problem with the data dictionary, when no such problem existed.
- InnoDB: The CHECK TABLE statement could fail for a large InnoDB table due to a timeout value of 2 hours. For typical storage devices, the issue could occur for tables that exceeded approximately 200 or 350 GB, depending on I/O speed. The fix relaxes the locking performed on the table being checked, which makes the timeout less likely. It also makes InnoDB recognize the syntax CHECK TABLE QUICK, which avoids the possibility of the timeout entirely.
- Replication: It was theoretically possible for concurrent execution of more than one instance of SHOW BINLOG EVENTS to crash the MySQL Server.
- Replication: Statements using AUTO_INCREMENT, LAST_INSERT_ID(), RAND(), or user variables could be applied in the wrong context on the slave when using statement-based replication and replication filtering server options
- Replication: An INSERT into a table that has a composite primary key that includes an AUTO_INCREMENT column that is not the first column of this composite key is not safe for statement-based binary logging or replication. Such statements are now marked as unsafe and fail with an error when using the STATEMENT binary logging format.
- SHOW TABLES was very slow unless the required information was already in the disk cache.
 OperaOpera 125.0 Build 5729.49 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 125.0 Build 5729.49 (64-bit) MalwarebytesMalwarebytes Premium 5.4.5
MalwarebytesMalwarebytes Premium 5.4.5 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.1 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2026 27.1 (64-bit) BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.153.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.42.153.1001 OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.6.3
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.6.3 PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders
TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders Edraw AIEdraw AI - AI-Powered Visual Collaboration
Edraw AIEdraw AI - AI-Powered Visual Collaboration


Comments and User Reviews