-
Latest Version
-
Operating System
Windows Vista / Windows 7 / Windows 8 / Windows 10 / Windows 11
-
User Rating
Click to vote -
Author / Product
-
Filename
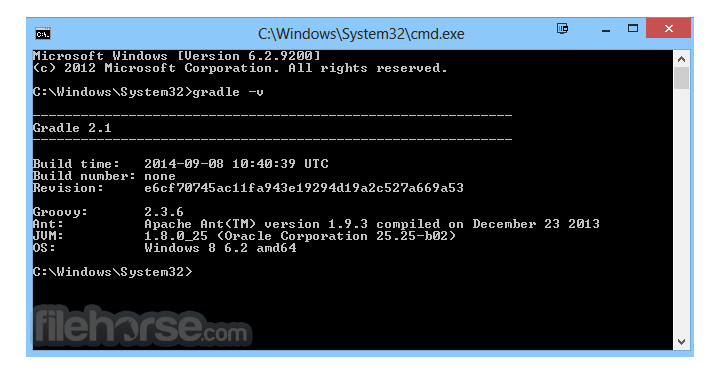
gradle-7.4-all.zip
Sometimes latest versions of the software can cause issues when installed on older devices or devices running an older version of the operating system.
Software makers usually fix these issues but it can take them some time. What you can do in the meantime is to download and install an older version of Gradle 7.4.
For those interested in downloading the most recent release of Gradle or reading our review, simply click here.
All old versions distributed on our website are completely virus-free and available for download at no cost.
We would love to hear from you
If you have any questions or ideas that you want to share with us - head over to our Contact page and let us know. We value your feedback!
What's new in this version:
New features and usability improvements:
Generate a single report for tests from multiple projects:
- By default, Gradle produces a separate HTML test report for every test task in each project. Previously, it was difficult to combine those reports across multiple projects in a safe and convenient way.
- This release adds the new test-report-aggregation plugin to make it easy to aggregate test results from multiple projects into a single HTML report. This plugin uses test suites registered with the jvm-test-suite plugin.
- When this plugin is applied to a Java project, Gradle will automatically create an aggregated test report for each test suite with test results from a compatible test suite in every project that the Java project depends on. See the sample in the user manual.
- If you want more control over the set of projects that are included in the aggregated report or which test suites are used, see another sample that requires you to provide this configuration in the user manual.
Generate a single JaCoCo code coverage from multiple projects:
- Gradle comes with a JaCoCo code coverage plugin that produces a coverage report for the built-in test task. Previously, it was difficult to combine such reports across multiple projects in a safe and convenient way.
- This release adds the new jacoco-report-aggregation plugin to make it easy to aggregate code coverage from multiple projects into a single report. This plugin uses test suites registered with the jvm-test-suite plugin.
- When this plugin is applied to a Java project, Gradle will automatically create an aggregated code coverage report for each test suite with code coverage data from a compatible test suite in every project that the Java project depends on. See the sample in the user manual.
- If you want more control over the set of projects that are included in the aggregated report or which test suites are used, see another sample that requires you to provide this configuration in the user manual.
Usability improvements:
Mark additional test source directories as tests in IntelliJ IDEA:
- The JVM Test Suite Plugin makes it easier to create additional sets of tests in a Java project.
- The IntelliJ IDEA Plugin plugin will now automatically mark all source directories used by a JVM Test Suite as test source directories within the IDE
- The Eclipse plugin will be updated in a future version of Gradle
- This change does not affect additional test source directories created in Android projects that will still need to be manually configured to be considered test directories. These test sources are not created using JVM test suites.
Type-safe accessors for extensions of repositories {} in Kotlin DSL:
- Starting with this version of Gradle, Kotlin DSL generates type-safe model accessors for custom extensions added to the repositories {} block. Custom extensions now have full content assist in the IDE.
Stable dependency verification file generation:
- Dependency verification allows Gradle to verify the checksums and signatures of the plugins and dependencies that are used by the build of your project to improve supply chain security.
- With this release, the generation of the dependency verification file has been improved to produce stable output. This means that Gradle will always produce the same output if the build configuration and the verification file did not change.
- This allows the the verification metadata generation feature to be used as a convenient update strategy. This is now a recommended way to update the dependency verification files.
Plugins can be declared with a version in a subproject in more cases:
- The plugins DSL provides a succinct and convenient way to declare plugin dependencies
- Previously, it was not possible to declare a plugin with a version in a subproject when the parent project also declared the same plugin. Now, this is allowed when Gradle can track the version of the plugin (currently when using included build plugins or externally resolved plugins), and the version of the plugin in both are the same.
- This change was required to allow the use of dependency catalog plugin aliases in both a parent and subproject's plugins {}
Changes following migration from AdoptOpenJDK to Adoptium:
- Java toolchains provide an easy way to declare which Java version your project should be built with. By default, Gradle will detect installed JDKs or automatically download new toolchain versions.
Following the migration of AdoptOpenJDK to Eclipse Adoptium, a number of changes have been made for toolchains:
- ADOPTIUM and IBM_SEMERU are now recognized as vendors
- Both of the above can be used as vendors and trigger auto-provisioning
- Using ADOPTOPENJDK as a vendor and having it trigger auto-provisioning will emit a deprecation warning
Configuration cache improvements:
- The configuration cache improves build time by caching the result of the configuration phase and reusing this for subsequent builds
- Automatic detection of environment variables, system properties and Gradle properties used at configuration time
- Previously, Gradle required build and plugin authors to use specific APIs to read external values such as environment variables, system properties and Gradle properties in order to take these values into consideration as configuration cache inputs. When one of those values changed, Gradle would re-execute the configuration phase of the build and create a new cache entry. Gradle also required marking external values used at configuration time with an explicit opt-in Provider.forUseAtConfigurationTime() API.
- This release makes it easier to adopt configuration cache by relaxing these requirements. Provider.forUseAtConfigurationTime() has been deprecated and external values can be read using standard Java and Gradle APIs. Environment variables, system properties and Gradle properties used at configuration time are automatically detected without requiring build or plugin authors to migrate to Gradle specific APIs. In case any of those inputs change, the configuration cache is invalidated automatically. Moreover, the detected configuration inputs are now presented in the configuration-cache HTML report to make it easier to investigate unexpected configuration cache misses.
Disable configuration caching when incompatible tasks are executed:
- The configuration cache works by caching the entire task graph for each set of requested tasks.
- Prior to this release, all tasks used by the project needed to be compatible with configuration cache before the configuration cache could be enabled
- It is now possible to declare that a particular task is not compatible with the configuration cache. Gradle will disable the configuration cache automatically whenever an incompatible task is scheduled to run. This makes it possible to enable the configuration cache without having to first migrate all tasks to be compatible. Builds will still benefit from the configuration cache when only compatible tasks are executed. This enables more gradual adoption of the configuration cache.
Other improvements:
Additional Gradle daemon debug options:
- The Gradle daemon can be started in a debug mode that allows you to connect a debugger to troubleshoot build scripts or plugin code execution. By default, Gradle assumes a particular set of debugging options.
- In this release, additional options have been added to specify the port, server mode, and suspend mode for the Gradle daemon. This is useful when the default options are not sufficient to connect to the Gradle daemon to debug build scripts or plugin code.
- This does not affect the debugging options used with --debug-jvm when used with Test or JavaExec tasks
Conflicts of precompiled plugins with core plugins is now an error:
- Precompiled plugins are plugins written in either Groovy or Kotlin DSLs. They are used to easily share build logic between projects using a DSL language and without the need to write a full plugin class.
- In previous versions, it was possible to name a precompiled plugin with a name that conflicted with any core plugin id. Since core plugins take precedence over other plugins this caused the precompiled plugin to be silently ignored.
- With this release, a name conflict between a precompiled plugin and a core plugin causes an error
Promoted features:
- Promoted features are features that were incubating in previous versions of Gradle but are now supported and subject to backwards compatibility. See the User Manual section on the “Feature Lifecycle” for more information.
- The following are the features that have been promoted in this Gradle release
Shared build services:
- Shared build services is promoted to a stable feature
Version catalogs:
- Version catalogs is promoted to a stable feature
Fixed:
93 issues have been fixed in Gradle 7.4:
- Update JvmTestSuite DSL Reference with Test Type Propery
- Custom test suite named unitTest conflicts with default test suite
- Inconsistent Javadoc annotations for org.gradle.api.tasks.testing.TestReport (gradle 7.4)
- Project dependency jar does not exist when resolving project dependency
- Gradle caches keyserver information even when it is disabled
- Configuration cache fails to serialize chain of mapped `Provider`s
- Configuration cache fails to store zipped `Provider`
- The IntelliJ IDEA Plugin does not mark JVM Test Suite sources as test source in the IDE
- jacoco-report-aggregation should gracefully handle missing execution data
- Aggregated test report does not respect java.testReportDir in some cases
- `notCompatibleWithConfigurationCache` and `org.gradle.unsafe.configuration-cache-problems=warn`
- Gradle dependency verification caches keys for too long
- Upgrade Gradle checks for Log4j 2.17.1
- Changes to toolChain implementation are ignored
- Java compiler constant analysis seems to be broken on 8u301
- Complete documentation for new aggregation plugins
- Fix links in new test suite samples
- Disk files cleanup on Teamcity causes problems with file system watching on Linux
- Add usage checks for verification variants - revised plan
- Missing Settings.includeFlat(Iterable<String>) method
- Revert usage of generic argument to objects.named extension in Kotlin samples and snippets, and build-logic scripts
- Documentation contains `{user-manual}` references causing malformed links
- Name conflict with new test suites and versionCatalog entry named `testing`
- Additional sanity checks for building variants
- Additional sanity checks for test suites - one suite per type per project
- Dependency verification does not find a verification-metadata entry on Android Studio sync
- Provider#map doesn't allows to transform into nullable type in Kotlin DSL
- ConcurrentModificationException during Ivy resolve
- Add Maven Toolchains support to Java Toolchains detection
- Configuration cache false positive when changing gradle.properties
- Configuration cache issue when loading JNA lib during configuration
- Problems reading data from Binary store when replacement rule is in place and original module has a dependency on the new module in POM file
- Remove ambiguity in overloaded AttributeContainer#attribute methods
- Only allow consumption of outgoing variants for Test Suites if feature preview flag is set
- Update outgoing variants for Test Suites and add additional sanity checking
- Guarantee new variants for test suites are not published
- Gradle 7.4 nightly breaks artifact transforms
- GenerateSourceRootsFile fails when buildSrc references included build
- Inconsistent behavior of versionCatalogs { } in buildSrc during IDEA sync
- Refactor `TestReport` task to support lazy wiring of inputs
- Broken links in 7.0 upgrade guide > custom build layout
- Is ConfigurableReport.setDestination(Provider) meant to be deprecated?
- Aggregate test results and coverage data from multiple projects
- Expose test results and JaCoCo coverage data as resolvable artifacts
- Allow tasks to consume outputs from tasks that produce verification failures
- Minor English improvements in the Structuring Large Projects example
- Clean up Javascript included in dependencies HTML report
- Deprecate tar tree without a backing file
- Expose outputs from Test tasks as variants to dependency management
- Add descriptions to build-init, testing-base, jvm-testing, testing-junit-platform subprojects
- Improve dependency verification file generation
- Provide alternative for flat project structure
- Upgrade Gradle wrapper task on Windows missing chars
- Missing Kotlin DSL overload on `DependencyHandler` for `ProviderConvertible`
- Doc outdated on embedded Kotlin
- Can't use library from version catalog in constraint if it has child aliases
- Build cache configuration is not inherited from top-level build in included build inside pluginManagement block
- Gradle dependency verification breaks Android Studio Gradle sync in an obscure way
- @Option on interfaces (implemented by tasks) is not respected
- Return of Problems reading data from Binary store
- 7.2: PluginDependenciesSpec interface adds non-default methods, thus breaking backward compatibility
- Gradle crashes when writing verification metadata
- Unexpected behavior of Java toolchains
- Multiple Publications warning specify names of overlapping publications
- Gradle module metadata publication should allow more formats
- Warn or fail when precompiled script plugin name collides with plugin ID
- Version Catalogs: Omit version for plugins already on the classpath
- Catalog version entry without version and `.withoutVersion()` call produces non-trivial errors
- Only modify task history in StoreExecutionStateStep
- Inconsistent name in TOML vs API. [libraries] versus findDependencies
- Allow JVM debug options to be configurable
- Toolchain: AdoptOpenJDK vendor rebranded to "Eclipse Foundation"
- Add Temurin to `JvmVendorSpec`
- "only id(String) method calls allowed in plugins {} script block" is not correct
- Random errors or build hanging forever with task outputs derived from a configuration
- Better Error reporting for name mismatch in catalog dependencies
- ScriptHandlerScope with configuration does not support version catalogs (MinimalExternalModuleDependency)
- Allow progressive adoption of the configuration cache
- Document requirements for concurrent access restrictions of shared build services
- Misleading error message when invalid blocks are placed before the plugins block in the settings file
- Configuration cache checks fingerprint of included build against properties from root build
- repositoriesMode FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS fails on IntelliJ import
- Timeouts when using the remote Build Cache in a GitHub workflow
- Leave comments and ordering untouched in the verification-metadata.xml file
- Document usage of `usesService` when working with build services
- Make --stacktrace and --full-stacktrace options available through gradle.properties
- finalizer tasks are not up to date when finalized tasks are up to date
- Add Settings.include(List) to include more than 250 subprojects in one call
- When 'clean' depends on another task, it can happen in the middle of a build, breaking it
- Use input snapshots to skip empty work
- Provide a declarative way to define separate test suites
- `gradle clean build` can run clean after tasks that produce output by depending on other tasks
- Gradle compile of groovy should not include grab/grapes annotation transform
 OperaOpera 117.0 Build 5408.39 (64-bit)
OperaOpera 117.0 Build 5408.39 (64-bit) PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025
PC RepairPC Repair Tool 2025 PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.4 (64-bit)
PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop CC 2025 26.4 (64-bit) OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum
OKXOKX - Buy Bitcoin or Ethereum iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.3.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure
iTop VPNiTop VPN 6.3.0 - Fast, Safe & Secure Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.1
Premiere ProAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2025 25.1 BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.41.661.1001
BlueStacksBlueStacks 10.41.661.1001 Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game
Hero WarsHero Wars - Online Action Game TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders
TradingViewTradingView - Trusted by 60 Million Traders LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2
LockWiperiMyFone LockWiper (Android) 5.7.2

Comments and User Reviews